Transient in utero disruption of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator causes phenotypic changes in alveolar type II cells in adult rats
- PMID: 19335897
- PMCID: PMC2675516
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2121-10-24
Transient in utero disruption of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator causes phenotypic changes in alveolar type II cells in adult rats
Abstract
Background: Mechanicosensory mechanisms regulate cell differentiation during lung organogenesis. We have previously demonstrated that cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) was integral to stretch-induced growth and development and that transient expression of antisense-CFTR (ASCFTR) had negative effects on lung structure and function. In this study, we examined adult alveolar type II (ATII) cell phenotype after transient knock down of CFTR by adenovirus-directed in utero expression of ASCFTR in the fetal lung.
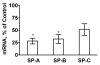
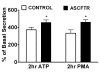
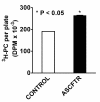
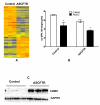
Results: In comparison to (reporter gene-treated) Controls, ASCFTR-treated adult rat lungs showed elevated phosphatidylcholine (PC) levels in the large but not in the small aggregates of alveolar surfactant. The lung mRNA levels for SP-A and SP-B were lower in the ASCFTR rats. The basal PC secretion in ATII cells was similar in the two groups. However, compared to Control ATII cells, the cells in ASCFTR group showed higher PC secretion with ATP or phorbol myristate acetate. The cell PC pool was also larger in the ASCFTR group. Thus, the increased surfactant secretion in ATII cells could cause higher PC levels in large aggregates of surfactant. In freshly isolated ATII cells, the expression of surfactant proteins was unchanged, suggesting that the lungs of ASCFTR rats contained fewer ATII cells. Gene array analysis of RNA of freshly isolated ATII cells from these lungs showed altered expression of several genes including elevated expression of two calcium-related genes, Ca2+-ATPase and calcium-calmodulin kinase kinase1 (CaMkk1), which was confirmed by real-time PCR. Western blot analysis showed increased expression of calmodulin kinase I, which is activated following phosphorylation by CaMkk1. Although increased expression of calcium regulating genes would argue in favor of Ca2+-dependent mechanisms increasing surfactant secretion, we cannot exclude contribution of alternate mechanisms because of other phenotypic changes in ATII cells of the ASCFTR group.
Conclusion: Developmental changes due to transient disruption of CFTR in fetal lung reflect in altered ATII cell phenotype in the adult life.
Figures




References
-
- Jiang X, Ingbar DH, O'Grady SM. Adrenergic regulation of ion transport across adult alveolar epithelial cells: effects on Cl- channel activation and transport function in cultures with an apical air interface. J Membr Biol. 2001;181:195–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

