Very old patients admitted to intensive care in Australia and New Zealand: a multi-centre cohort analysis
- PMID: 19335921
- PMCID: PMC2689489
- DOI: 10.1186/cc7768
Very old patients admitted to intensive care in Australia and New Zealand: a multi-centre cohort analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Older age is associated with higher prevalence of chronic illness and functional impairment, contributing to an increased rate of hospitalization and admission to intensive care. The primary objective was to evaluate the rate, characteristics and outcomes of very old (age >or= 80 years) patients admitted to intensive care units (ICUs).
Methods: Retrospective analysis of prospectively collected data from the Australian New Zealand Intensive Care Society Adult Patient Database. Data were obtained for 120,123 adult admissions for >or= 24 hours across 57 ICUs from 1 January 2000 to 31 December 2005.
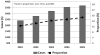
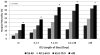
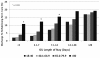
Results: A total of 15,640 very old patients (13.0%) were admitted during the study. These patients were more likely to be from a chronic care facility, had greater co-morbid illness, greater illness severity, and were less likely to receive mechanical ventilation. Crude ICU and hospital mortalities were higher (ICU: 12% vs. 8.2%, P < 0.001; hospital: 24.0% vs. 13%, P < 0.001). By multivariable analysis, age >/= 80 years was associated with higher ICU and hospital death compared with younger age strata (ICU: odds ratio (OR) = 2.7, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 2.4 to 3.0; hospital: OR = 5.4, 95% CI = 4.9 to 5.9). Factors associated with lower survival included admission from a chronic care facility, co-morbid illness, nonsurgical admission, greater illness severity, mechanical ventilation, and longer stay in the ICU. Those aged >or= 80 years were more likely to be discharged to rehabilitation/long-term care (12.3% vs. 4.9%, OR = 2.7, 95% CI = 2.6 to 2.9). The admission rates of very old patients increased by 5.6% per year. This potentially translates to a 72.4% increase in demand for ICU bed-days by 2015.
Conclusions: The proportion of patients aged >or= 80 years admitted to intensive care in Australia and New Zealand is rapidly increasing. Although these patients have more co-morbid illness, are less likely to be discharged home, and have a greater mortality than younger patients, approximately 80% survive to hospital discharge. These data also imply a potential major increase in demand for ICU bed-days for very old patients within a decade.
Figures


Comment in
-
Oncoming tides in the Age(ing) of Aquarius.Crit Care. 2009;13(3):145. doi: 10.1186/cc7791. Epub 2009 May 15. Crit Care. 2009. PMID: 19490598 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Population Division, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, United Nations World Population Ageing 1950–2050 http://www.un.org/esa/population/publications/worldageing19502050/
-
- Song X, MacKnight C, Latta R, Mitnitski AB, Rockwood K. Frailty and survival of rural and urban seniors: results from the Canadian Study of Health and Aging. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2007;19:145–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

