Biochemistry, physiology, and genetics of GPAT, AGPAT, and lipin enzymes in triglyceride synthesis
- PMID: 19336658
- PMCID: PMC2692402
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.90958.2008
Biochemistry, physiology, and genetics of GPAT, AGPAT, and lipin enzymes in triglyceride synthesis
Abstract
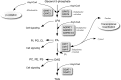
Triacylglycerol (TAG) synthesis and storage in tissues such as adipose tissue and liver have important roles in metabolic homeostasis. The molecular identification of genes encoding enzymes that catalyze steps in TAG biosynthesis from glycerol 3-phosphate has revealed an unexpected number of protein isoforms of the glycerol phosphate acyltransferase (GPAT), acylglycerolphosphate acyltransferase (AGPAT), and lipin (phosphatidate phosphatase) families that appear to catalyze similar biochemical reactions. However, on the basis of available data for a few members in which genetic deficiencies in mouse and/or human have been studied, we postulate that each GPAT, AGPAT, and lipin family member likely has a specialized role that may be uncovered through careful biochemical and physiological analyses.
Figures

References
-
- Agarwal AK, Arioglu E, De Almeida S, Akkoc N, Taylor SI, Bowcock AM, Barnes RI, Garg A. AGPAT2 is mutated in congenital generalized lipodystrophy linked to chromosome 9q34. Nat Genet 31: 21–23, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal AK, Barnes RI, Garg A. Functional characterization of human 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase isoform 8: cloning, tissue distribution, gene structure, and enzymatic activity. Arch Biochem Biophys 449: 64–76, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal AK, Garg A. Congenital generalized lipodystrophy: significance of triglyceride biosynthetic pathways. Trends Endocrinol Metab 14: 214–221, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal AK, Garg A. Genetic basis of lipodystrophies and management of metabolic complications. Annu Rev Med 57: 297–311, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal AK, Garg A. Genetic disorders of adipose tissue development, differentiation, and death. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 7: 175–199, 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

