Intratracheal gene transfer of adrenomedullin using polyplex nanomicelles attenuates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats
- PMID: 19337232
- PMCID: PMC2835223
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2009.63
Intratracheal gene transfer of adrenomedullin using polyplex nanomicelles attenuates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats
Abstract
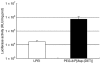
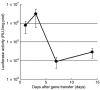
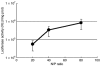
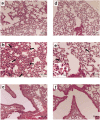
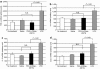
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a life-threatening disease characterized by progressive PAH and right ventricular failure. Despite recent advances in therapeutic approaches using prostanoids, endothelin antagonists, and so on, PAH remains a challenging condition. To develop a novel therapeutic approach, we have established a nonviral gene delivery system of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)-based block catiomers, which form a polyplex nanomicelle with a nanoscaled core-shell structure in the presence of DNA. The polyplex nanomicelle from PEG-b-poly{N-[N-(2-aminoethyl)-2-aminoethyl]aspartamide} (PEG-b-P[Asp(DET)]), having ethylenediamine units at the side chain, showed ~100-fold increase in luciferase transgene expression activity in mouse lung via intratracheal administration with a minimal toxicity compared with the polyplex from linear poly(ethylenimine) (LPEI). The transfection activity was highest on day 3 after administration and remained detectable until day 14. PEG-b-P[Asp(DET)] polyplex nanomicelles were formulated with a therapeutic plasmid bearing the human adrenomedullin (AM) gene and intratracheally administered to rats with monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension. The right ventricular pressure significantly decreased 3 days after administration as confirmed by a notable increase of pulmonary human AM mRNA levels. Intratracheal administration of PEG-b-P[Asp-(DET)] polyplex nanomicelles showed remarkable therapeutic efficacy with PAH animal models without compromising biocompatibility.
Figures


References
-
- Rubin LJ. Pulmonary arterial hypertension. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2006;3:111–115. - PubMed
-
- Badesch DB, Abman SH, Ahearn GS, Barst RJ, McCrory DC, Simonneau G, et al. Medical therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines Chest 200412635S–62S.1 Suppl - PubMed
-
- D'Alonzo GE, Barst RJ, Ayres SM, Bergofsky EH, Brundage BH, Detre KM, et al. Survival in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Results from a national prospective registry. Ann Intern Med. 1991;115:343–349. - PubMed
-
- Kitamura K, Kangawa K, Kawamoto M, Ichiki Y, Nakamura S, Matsuo H, et al. Adrenomedullin: a novel hypotensive peptide isolated from human pheochromocytoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;192:553–560. - PubMed
-
- Kitamura K, Kangawa K., and , Eto T. Adrenomedullin and PAMP: discovery, structures, and cardiovascular functions. Microsc Res Tech. 2002;57:3–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

