VEGFA upregulates FLJ10540 and modulates migration and invasion of lung cancer via PI3K/AKT pathway
- PMID: 19337377
- PMCID: PMC2659802
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005052
VEGFA upregulates FLJ10540 and modulates migration and invasion of lung cancer via PI3K/AKT pathway
Abstract
Background: Lung adenocarcinoma is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths among both men and women in the world. Despite recent advances in diagnosis and treatment, the mortality rates with an overall 5-year survival of only 15%. This high mortality is probably attributable to early metastasis. Although several well-known markers correlated with poor/metastasis prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma patients by immunohistochemistry was reported, the molecular mechanisms of lung adenocarcinoma development are still not clear. To explore novel molecular markers and their signaling pathways will be crucial for aiding in treatment of lung adenocarcinoma patients.
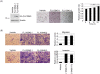
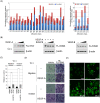
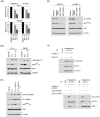
Methodology/principal findings: To identify novel lung adenocarcinoma-associated /metastasis genes and to clarify the underlying molecular mechanisms of these targets in lung cancer progression, we created a bioinformatics scheme consisting of integrating three gene expression profile datasets, including pairwise lung adenocarcinoma, secondary metastatic tumors vs. benign tumors, and a series of invasive cell lines. Among the novel targets identified, FLJ10540 was overexpressed in lung cancer tissues and is associated with cell migration and invasion. Furthermore, we employed two co-expression strategies to identify in which pathway FLJ10540 was involved. Lung adenocarcinoma array profiles and tissue microarray IHC staining data showed that FLJ10540 and VEGF-A, as well as FLJ10540 and phospho-AKT exhibit positive correlations, respectively. Stimulation of lung cancer cells with VEGF-A results in an increase in FLJ10540 protein expression and enhances complex formation with PI3K. Treatment with VEGFR2 and PI3K inhibitors affects cell migration and invasion by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Moreover, knockdown of FLJ10540 destabilizes formation of the P110-alpha/P85-alpha-(PI3K) complex, further supporting the participation of FLJ10540 in the VEGF-A/PI3K/AKT pathway.
Conclusions/significance: This finding set the stage for further testing of FLJ10540 as a new therapeutic target for treating lung cancer and may contribute to the development of new therapeutic strategies that are able to block the PI3K/AKT pathway in lung cancer cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

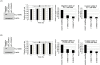

References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- GA KBaP. Surgical management of non-small cell lung cancer. Pearson's Thoracic & Esophageal Surgery. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone/ Elsevier; 2008. pp. 765–780.
-
- Friedl P, Wolf K. Tumour-cell invasion and migration: diversity and escape mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:362–374. - PubMed
-
- Hendrix MJ, Seftor EA, Chu YW, Trevor KT, Seftor RE. Role of intermediate filaments in migration, invasion and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1996;15:507–525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

