Illicit organogenesis: Methods and substances of doping and manipulation
- PMID: 19337407
- PMCID: PMC2634332
- DOI: 10.4161/org.4.4.7286
Illicit organogenesis: Methods and substances of doping and manipulation
Abstract
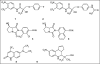
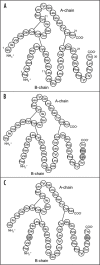
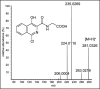
Doping and manipulation are undesirable companions of professional and amateur sport. Numerous adverse analytical findings as well as confessions of athletes have demonstrated the variety of doping agents and methods as well as the inventiveness of cheating sportsmen. Besides 'conventional' misuse of drugs such as erythropoietin and insulins, experts fear that therapeutics that are currently undergoing clinical trials might be part of current or future doping regimens, which aim for an increased functionality and performance or organs and tissues. Emerging drugs such as selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs), hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) complex stabilizers or modulators of muscle fiber calcium channels are considered relevant for current and future doping controls due to their high potential for misuse in sports.
Keywords: HIF; S107; anabolics; doping; insulin; mass spectrometry; sport.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of SARMs in doping control analysis.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2018 Mar 15;464:34-45. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2017.01.040. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 28137616 Review.
-
Emerging drugs: mechanism of action, mass spectrometry and doping control analysis.J Mass Spectrom. 2009 Apr;44(4):442-60. doi: 10.1002/jms.1584. J Mass Spectrom. 2009. PMID: 19373874
-
Mass spectrometric characterization of the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) stabilizer drug candidate BAY 85-3934 (molidustat) and its glucuronidated metabolite BAY-348, and their implementation into routine doping controls.Drug Test Anal. 2017 Jan;9(1):61-67. doi: 10.1002/dta.2011. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Drug Test Anal. 2017. PMID: 27346747
-
Analytical approaches for the detection of emerging therapeutics and non-approved drugs in human doping controls.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Dec;101:66-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2014.05.020. Epub 2014 May 23. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 24906629 Review.
-
Mass spectrometric studies on selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) using electron ionization and electrospray ionization/collision-induced dissociation.Eur J Mass Spectrom (Chichester). 2018 Feb;24(1):145-156. doi: 10.1177/1469066717731228. Epub 2017 Sep 13. Eur J Mass Spectrom (Chichester). 2018. PMID: 29232975
Cited by
-
'Blood doping' from Armstrong to prehabilitation: manipulation of blood to improve performance in athletes and physiological reserve in patients.Extrem Physiol Med. 2016 Feb 29;5:5. doi: 10.1186/s13728-016-0046-0. eCollection 2016. Extrem Physiol Med. 2016. PMID: 26929820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The androgen receptor and its use in biological assays: looking toward effect-based testing and its applications.J Anal Toxicol. 2011 Nov;35(9):594-607. doi: 10.1093/anatox/35.9.594. J Anal Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 22080898 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Toohey K, Veal AJ. The Olympic Games—A social science perspective. Oxon—New York: CABI Publishing; 2000.
-
- World Anti-Doping Agency, author. The 2008 Prohibited List. 2008. www.wada-ama.org/rtecontent/document/2008_List_En.pdf.
-
- Lasne F, Martin L, Crepin N, de Ceaurriz J. Detection of isoelectric profiles of erythropoietin in urine: differentiation of natural and administered recombinant hormones. Anal Biochem. 2002;311:119–126. - PubMed
-
- Lasne F, de Ceaurriz J. Recombinant erythropoietin in urine. Nature. 2000;405:635. - PubMed
-
- Thevis M, Schänzer W. Identification and Characterization of Peptides and Proteins in Doping Control Analysis. Curr Proteomics. 2005;2:191–208.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
