Illicit organogenesis: Methods and substances of doping and manipulation
- PMID: 19337407
- PMCID: PMC2634332
- DOI: 10.4161/org.4.4.7286
Illicit organogenesis: Methods and substances of doping and manipulation
Abstract
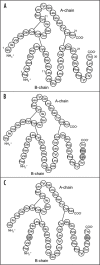
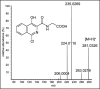
Doping and manipulation are undesirable companions of professional and amateur sport. Numerous adverse analytical findings as well as confessions of athletes have demonstrated the variety of doping agents and methods as well as the inventiveness of cheating sportsmen. Besides 'conventional' misuse of drugs such as erythropoietin and insulins, experts fear that therapeutics that are currently undergoing clinical trials might be part of current or future doping regimens, which aim for an increased functionality and performance or organs and tissues. Emerging drugs such as selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs), hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) complex stabilizers or modulators of muscle fiber calcium channels are considered relevant for current and future doping controls due to their high potential for misuse in sports.
Keywords: HIF; S107; anabolics; doping; insulin; mass spectrometry; sport.
Figures
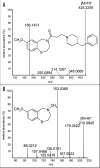
References
-
- Toohey K, Veal AJ. The Olympic Games—A social science perspective. Oxon—New York: CABI Publishing; 2000.
-
- World Anti-Doping Agency, author. The 2008 Prohibited List. 2008. www.wada-ama.org/rtecontent/document/2008_List_En.pdf.
-
- Lasne F, Martin L, Crepin N, de Ceaurriz J. Detection of isoelectric profiles of erythropoietin in urine: differentiation of natural and administered recombinant hormones. Anal Biochem. 2002;311:119–126. - PubMed
-
- Lasne F, de Ceaurriz J. Recombinant erythropoietin in urine. Nature. 2000;405:635. - PubMed
-
- Thevis M, Schänzer W. Identification and Characterization of Peptides and Proteins in Doping Control Analysis. Curr Proteomics. 2005;2:191–208.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
