Comparison between dynamic contour tonometry and Goldmann applanation tonometry
- PMID: 19337476
- PMCID: PMC2655749
- DOI: 10.3341/kjo.2009.23.1.27
Comparison between dynamic contour tonometry and Goldmann applanation tonometry
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the intraocular pressures (IOPs) measured by dynamic contour tonometry (DCT) and Goldmann applanation tonometry (GAT), and to investigate the association of IOPs on eyes of varying central corneal thickness (CCT).
Methods: In this prospective study, 451 eyes of 233 subjects were enrolled. IOPs were measured by GAT and DCT. CCT was measured three times and the average was calculated. Each eye was classified into one of three groups according to CCT: low CCT (group A, CCT<520 microm, n=146); normal CCT (group B, 520 microm<or=CT<or=550 microm, n=163); and high CCT (group C, CCT>550 microm, n=142). In each group, we investigated the association of CCT with IOP measurement by GAT and DCT.
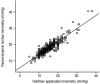
Results: The IOPs measured by GAT and DCT were significantly associated for all eyes (R=0.853, p<0.001, Pearson correlation). CCT was related with both IOP measurement by GAT and DCT with statistical significance (mixed effect model, p<0.001). However, subgroup analysis showed that CCT affected IOP measured by GAT for groups B and C, whereas it affected IOP measured by DCT only for group C.
Conclusions: IOP measured by DCT was not affected by CCT in eyes with low to normal CCT, whereas this measurement was affected in eyes of high CCT range. CCT may have less effect on IOP measurements using DCT than those obtained by GAT, within a specified range of CCT.
Keywords: Central corneal thickness; Dynamic contour tonometry; Goldmann applanation tonometry.
Figures
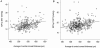
References
-
- Allingham R, Damji K, Freedman S, et al. Intraocular Pressure and Tonometry. In: Allingham RR, Damji K, Freedman S, et al., editors. Shields' Textbook of Glaucoma. fifth ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005. chap. 2.
-
- Zhang H, Xu L, Chen C, Jonas JB. Central corneal thickness in adult Chinese. Association with ocular and general parameters. The Beijing Eye Study. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2008;246:587–592. - PubMed
-
- Kanngiesser HE, Kniestedt C, Robert YC. Dynamic contour tonometry: presentation of a new tonometer. J Glaucoma. 2005;14:344–350. - PubMed
-
- Kaufmann C, Bachmann LM, Thiel MA. Comparison of dynamic contour tonometry with Goldmann applanation tonometry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004;45:3118–3121. - PubMed
-
- Schneider E, Grehn F. Intraocular pressure measurement - comparison of dynamic contour tonometry and goldmann applanation tonometry. J glaucoma. 2006;15:2–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical