The effects of prior calcium channel blocker therapy on creatine kinase-MB levels after percutaneous coronary interventions
- PMID: 19337554
- PMCID: PMC2663464
- DOI: 10.2147/vhrm.s2998
The effects of prior calcium channel blocker therapy on creatine kinase-MB levels after percutaneous coronary interventions
Abstract
Background: Use of intracoronary calcium channel blockers (CCBs) during percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) has been shown to have favorable effects on coronary blood flow. We aimed to investigate the effects of CCBs administrated perorally on creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB) levels in patients undergoing elective PCI.
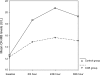
Methods: A total of 570 patients who underwent PCI were evaluated for CK-MB elevation. Patients who were on CCB therapy when admitted to the hospital constituted the CCB group. No CCBs were given to the rest of the patients during the periprocedural period and these patients served as the control group. Blood samples for CK-MB were obtained before and at 6 h, 24 h, and 36 h after the procedure.
Results: 217 patients were in the CCB group (mean age 60.2 +/- 9.3 years, 162 males), and 353 were in the control group (mean age 60.0 +/- 10.1 years, 262 males). CK-MB levels increased above the normal values in 41 patients (18.9%) of the CCBs group and in 97 patients (27.5%) of the control group (p = 0.02). Median CK-MB levels were significantly higher in the control group for all studied hours (for all p < 0.05).
Conclusions: Prior oral CCB therapy may have favorable effects in preventing myocyte necrosis after elective PCI.
Keywords: calcium channel blockers; myonecrosis; percutaneous coronary interventions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of intracoronary nicardipine on cardiac enzymes after elective percutaneous coronary intervention.Clin Cardiol. 2009 Jun;32(6):315-20. doi: 10.1002/clc.20580. Clin Cardiol. 2009. PMID: 19569065 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of persistent platelet reactivity despite aspirin therapy on cardiac troponin I and creatine kinase-MB levels after elective percutaneous coronary interventions.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2008 Jun;25(3):239-46. doi: 10.1007/s11239-007-0067-z. Epub 2007 Jun 16. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2008. PMID: 17574519 Clinical Trial.
-
The assessment of Shin's method for the prediction of creatinine kinase-MB elevation after percutaneous coronary intervention: an intravascular ultrasound study.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011 Jul;27(6):883-92. doi: 10.1007/s10554-010-9734-9. Epub 2010 Oct 24. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011. PMID: 20972833
-
Prognostic value of creatine kinase-myocardial band isoenzyme elevation following percutaneous coronary intervention: a meta-analysis.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2013 May;81(6):959-67. doi: 10.1002/ccd.24542. Epub 2012 Nov 14. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2013. PMID: 22744792 Review.
-
[Prevention of periprocedural myocardial damage in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention].Ital Heart J Suppl. 2005 Sep;6(9):553-60. Ital Heart J Suppl. 2005. PMID: 16281714 Review. Italian.
References
-
- Abdelmeguid AE, Topol EJ, Whitlow PL, et al. Significance of mild transient release of creatine kinase-MB fraction after percutaneous coronary interventions. Circulation. 1996;94:1528–36. - PubMed
-
- Abdelmeguid AE, Topol EJ. The myth of the myocardial ‘infarctlet’ during percutaneous coronary revascularization procedures. Circulation. 1996;94:3369–75. - PubMed
-
- Akkerhuis KM, Alexander JH, Tardiff BE, et al. Minor myocardial damage and prognosis. Circulation. 2002;105:554–6. - PubMed
-
- Aronow HD, McRae T, Quinn MJ. Patients on lipid-lowering therapy at the time of myocardial infarction have smaller infarcts: further evidence to suggest a salutary effect in acute coronary syndrome [abstract] J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002b;39:318A.
-
- Aronow HD, Quinn MJ, Gurm HS. Myocardial necrosis is halved in patients undergoing elective percutaneous coronary intervention who are pretreated with lipid-lowering therapy [abstract] J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002a;39:32A.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous