Effect of conjugated linoleic acid, vitamin E and their combination on lipid profiles and blood pressure of Iranian adults with active rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 19337555
- PMCID: PMC2663461
- DOI: 10.2147/vhrm.s3822
Effect of conjugated linoleic acid, vitamin E and their combination on lipid profiles and blood pressure of Iranian adults with active rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
The aim of this study was to assess the impact of conjugated linoleic acids (CLAs), vitamin E, and combination of these nutrients on serum lipid profiles and blood pressure (BP) in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, 87 patients with active RA were divided into four groups receiving one of the following daily supplements for three months: Group C: CLAs 2.5 g equivalent to 2 g mixture of cis 9-trans 11 and trans 10-cis12 CLAs in a rate of 50/50; Group E: vitamin E: 400 mg; Group CE: CLAs and vitamin E at above doses: Group P: placebo. After supplementation, SBP levels decreased significantly in the group C in comparison with groups E and P and mean arterial pressure reduced significantly in groups C and CE. There weren't significant differences in the levels of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), triglycerides, cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), LDL/HDL, cholesterol/HDL, fasting blood sugar, C-reactive protein (CRP), arylestrase activity, platelet count and body mass index between groups. CRP dropped nonsignificantly in groups P, C, E and CE (19%, 24%, 55%, and 39%, respectively). Erythrocytes sedimentation rate levels decreased in groups C, E and CE (P < or = 0.05, P < or = 0.05, P < or = 0.001, respectively). It is concluded that supplementation of CLAs decreased BP and vitamin E decreased CRP. Therefore co-supplementation of CLAs and vitamin E might be profitable for heart disease prevention in RA patients.
Keywords: blood pressure; conjugated linoleic acids; lipid profiles; rheumatoid arthritis; vitamin E.
Figures
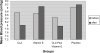

Similar articles
-
Effect of conjugated linoleic Acid, vitamin e, alone or combined on immunity and inflammatory parameters in adults with active rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized controlled trial.Int J Prev Med. 2014 Dec;5(12):1567-77. Int J Prev Med. 2014. PMID: 25709792 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of conjugated linoleic acids, vitamin E and their combination on the clinical outcome of Iranian adults with active rheumatoid arthritis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2009 Apr;12(1):20-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1756-185X.2009.01374.x. Int J Rheum Dis. 2009. PMID: 20374312 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Sesamin Supplementation on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Am Coll Nutr. 2016 May-Jun;35(4):300-7. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2015.1005198. Epub 2015 Jul 7. J Am Coll Nutr. 2016. PMID: 26151734 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E co-supplementation on gene expression of lipoprotein(a) and oxidized low-density lipoprotein, lipid profiles and biomarkers of oxidative stress in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017 Jan 5;439:247-255. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2016.09.008. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 27619403 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of vitamin D supplementation on serum lipid profiles: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Nutr Rev. 2019 Dec 1;77(12):890-902. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuz037. Nutr Rev. 2019. PMID: 31407792
Cited by
-
The effect of conjugated linoleic acid supplementation in comparison with omega-6 and omega-9 on lipid profile: a graded, dose-response systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Nutr. 2024 Mar 19;11:1336889. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1336889. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38567248 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Vitamin E Supplementation on Blood Pressure and Hs-CRP in Type 2 Diabetic Patients | doi: 10.5681/hpp.2012.009.Health Promot Perspect. 2012 Jul 1;2(1):72-9. eCollection 2012. Health Promot Perspect. 2012. PMID: 24688920 Free PMC article.
-
Conjugated Linoleic Acid Supplementation has no Impact on Aerobic Capacity of Healthy Young Men.Lipids. 2015 Aug;50(8):805-9. doi: 10.1007/s11745-015-4031-y. Epub 2015 May 24. Lipids. 2015. PMID: 26003683 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of conjugated linoleic Acid, vitamin e, alone or combined on immunity and inflammatory parameters in adults with active rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized controlled trial.Int J Prev Med. 2014 Dec;5(12):1567-77. Int J Prev Med. 2014. PMID: 25709792 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of conjugated linoleic acid supplementation on lipid profile in adults: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis.Front Nutr. 2022 Nov 3;9:953012. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.953012. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36438733 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aldred S, Sozzi T, Mudway I, et al. Alpha tocopherol supplementation elevates plasma apolipoprotein A1 isoforms in normal healthy subjects. Proteomics. 2006;6:1695–703. - PubMed
-
- Alice V, da Costa V, Vianna LM. Effect of α-tocopherol supplementation on blood pressure and lipidic profile in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clinica Chimica Acta. 2005;351:101–4. - PubMed
-
- Arbonés-Mainar JM, Navarro MA, Guzmán MA, et al. Selective effect of conjugated linoleic acid isomers on atherosclerotic lesion development in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Atherosclerosis. 2006;189:318–27. - PubMed
-
- Arnett F, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, et al. The American Rheumatoid Association 1987 revised criteria for the Classification of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;24:315–24. - PubMed
-
- Basu S, Smedman A, Vessby B. Conjugated linoleic acid induces lipid peroxidation in humans. FEBS Lett. 2000b;468:33–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

