Do Estrogen Receptor beta Polymorphisms Play A Role in the Pharmacogenetics of Estrogen Signaling?
- PMID: 19337586
- PMCID: PMC2662734
- DOI: 10.2174/187569208786733820
Do Estrogen Receptor beta Polymorphisms Play A Role in the Pharmacogenetics of Estrogen Signaling?
Abstract
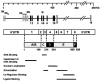
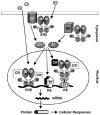
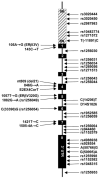
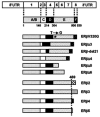
Estrogen hormones play critical roles in the regulation of many tissue functions. The effects of estrogens are primarily mediated by the estrogen receptors (ER) alpha and beta. ERs are ligand-activated transcription factors that regulate a complex array of genomic events that orchestrate cellular growth, differentiation and death. Although many factors contribute to their etiology, estrogens are thought to be the primary agents for the development and/or progression of target tissue malignancies. Many of the current modalities for the treatment of estrogen target tissue malignancies are based on agents with diverse pharmacology that alter or prevent ER functions by acting as estrogen competitors. Although these compounds have been successfully used in clinical settings, the efficacy of treatment shows variability. An increasing body of evidence implicates ERalpha polymorphisms as one of the contributory factors for differential responses to estrogen competitors. This review aims to highlight the recent findings on polymorphisms of the lately identified ERbeta in order to provide a functional perspective with potential pharmacogenomic implications.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ali S, Coombes RC. Endocrine-responsive breast cancer and strategies for combating resistance. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:101–112. - PubMed
-
- Almeida S, Franken N, Zandona MR, Osorio-Wender MC, Hutz MH. Estrogen receptor 2 and progesterone receptor gene polymorphisms and lipid levels in women with different hormonal status. Pharmacogenomics J. 2005;5:30–34. - PubMed
-
- Ansonoff MA, Etgen AM. Estradiol elevates protein kinase C catalytic activity in the preoptic area of female rats. Endocrinology. 1998;139:3050–3056. - PubMed
-
- Arko B, Prezelj J, Komel R, Kocijancic A, Marc J. No major effect of estrogen receptor β gene RsaI polymorphism on bone mineral density and response to alendronate therapy in post-menopausal osteoporosis. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2002;81:147–152. - PubMed
-
- Aschim EL, Giwercman A, Stahl O, Eberhard J, Cwikiel M, Nordenskjold A, Haugen TB, Grotmol T, Giwercman YL. The RsaI polymorphism in the estrogen receptor-β gene is associated with male infertility. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:5343–5348. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
