Accurate and sensitive peptide identification with Mascot Percolator
- PMID: 19338334
- PMCID: PMC2734080
- DOI: 10.1021/pr800982s
Accurate and sensitive peptide identification with Mascot Percolator
Abstract
Sound scoring methods for sequence database search algorithms such as Mascot and Sequest are essential for sensitive and accurate peptide and protein identifications from proteomic tandem mass spectrometry data. In this paper, we present a software package that interfaces Mascot with Percolator, a well performing machine learning method for rescoring database search results, and demonstrate it to be amenable for both low and high accuracy mass spectrometry data, outperforming all available Mascot scoring schemes as well as providing reliable significance measures. Mascot Percolator can be readily used as a stand alone tool or integrated into existing data analysis pipelines.
Figures


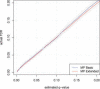
References
-
- Hunt DF, Henderson RA, Shabanowitz J, Sakaguchi K, Michel H, Sevilir N, Cox AL, Appella E, Engelhard VH. Characterization of peptides bound to the class I MHC molecule HLA-A2.1 by mass spectrometry. Science. 1992;255:1261–1263. - PubMed
-
- Wolters DA, Washburn MP, Yates JR., III An automated multidimensional protein identification technology for shotgun proteomics. Anal. Chem. 2001;73:5683–5690. - PubMed
-
- Desiere F, Deutsch EW, Nesvizhskii AI, Mallick P, King NL, Eng JK, Aderem A, Boyle R, Brunner E, Donohoe S, Fausto N, Hafen E, Hood L, Katze MG, Kennedy KA, Kregenow F, Lee H, Lin B, Martin D, Ranish JA, Rawlings DJ, Samelson LE, Shiio Y, Watts JD, Wollscheid B, Wright ME, Yan W, Yang L, Yi EC, Zhang H, Aebersold R. Integration with the human genome of peptide sequences obtained by high-throughput mass spectrometry. Genome Biol. 2005;6:R9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Foster LJ, de Hoog CL, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Xie X, Mootha VK, Mann M. A mammalian organelle map by protein correlation profiling. Cell. 2006;125:187–199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

