IL-2 and antigen dose differentially regulate perforin- and FasL-mediated cytolytic activity in antigen specific CD4+ T cells
- PMID: 19338979
- PMCID: PMC2683476
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2009.03.002
IL-2 and antigen dose differentially regulate perforin- and FasL-mediated cytolytic activity in antigen specific CD4+ T cells
Abstract
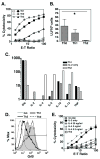
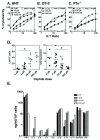
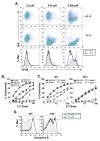
CD4 T cell effectors can promote survival against lethal influenza virus via perforin mediated cytolytic mechanisms; however, our understanding of how naïve CD4 cells differentiate into class II restricted killers remains obscure. To address this, TCR Tg CD4 cells were activated in vitro and examined for their ability to lyse target cells. We found that cytokine polarized CD4 T cell effectors displayed cytolytic activity with the hierarchy Th0>Th1>Th2. Further, IL-4 inhibited the generation of cytotoxic CD4 cells. LPS stimulated B cells and bone marrow derived dendritic cells (BMDC) both induced potent cytolytic activity; however, IL-6, TGF-beta, IL-10, IL-12 or TNF-alpha were not required for inducing cytolytic activity in CD4 effectors. Antigen dose had a marked effect on cytotoxicity: low concentrations of peptide induced more potent cytolytic activity than relatively high concentrations. At low peptide concentration, exogenous IL-2 was necessary to drive granzyme B (GrB) expression and perforin mediated lysis. Thus, low antigen dose and early activation signals via IL-2 direct the CD4 T cell response toward effectors with perforin mediated cytolytic potential. These data have implications for the design of vaccines that may induce cytolytic CD4 cells in vivo and improve cell-mediated immunity to viral and bacterial infections.
Figures
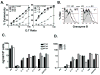

References
-
- McHeyzer-Williams LJ, McHeyzer-Williams MG. Antigen-specific memory B cell development. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:487–513. - PubMed
-
- Bennett SRM, Carbone FR, Karamalis F, Flavell RA, Miller JFAP, Heath WR. Help for cytotoxic-T-cell responses is mediated by CD40 signalling. Nature. 1998;393:478–480. - PubMed
-
- Ridge JP, Di Rosa F, Matzinger P. A conditioned dendritic cell can be a temporal bridge between a CD4+ T-helper and a T-killer cell [see comments] Nature. 1998;393:474–8. - PubMed
-
- Schoenberger SP, Toes REM, van der Voort EIH, Offringa R, Melief CJM. T-cell help for cytotoxic T lymphocytes is mediated by CD40-CD40L interactions. Nature. 1998;393:480–483. - PubMed
-
- Shedlock DJ, Shen H. Requirement for CD4 T cell help in generating functional CD8 T cell memory. Science. 2003;300:337–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

