A web application for moderation training: initial results of a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 19339137
- PMCID: PMC2739257
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsat.2009.03.001
A web application for moderation training: initial results of a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
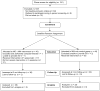
Eighty-four heavy drinkers who responded to a newspaper recruitment advertisement were randomly assigned to receive either (a) training in a Moderate Drinking protocol via an Internet-based program (www.moderatedrinking.com) and use of the online resources of Moderation Management (MM; www.moderation.org) or (b) use of the online resources of MM alone. Follow-ups are being conducted at 3, 6, and 12 months. Results of the recently completed 3-month follow-up (86% follow-up) indicated both groups significantly reduced their drinking based on these variables: standard drinks per week, percent days abstinent, and mean estimated blood alcohol concentration (BAC) per drinking day. Both groups also significantly reduced their alcohol-related problems. Relative to the control group, the experimental group had better outcomes on percent days abstinent and log drinks per drinking day. These short-term outcome data provide evidence for the effectiveness of both the Moderate Drinking Web application and of the resources available online at MM in helping heavy drinkers reduce their drinking and alcohol-related problems.
Figures


References
-
- Calbring P, Smit F. Randomized trial of internet-delivered self-help with telephone support for pathological gamblers. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 2008;76 (6):1090–1094. - PubMed
-
- Cohen S. Measuring the functional components of social support. In: Sarason IG, Sarason BR, editors. Social Support: Theory, Research and Applications. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Martinus Nijhoff; 1985. pp. 73–94.
-
- Derogatis LR. BSI-18: Administration, Scoring and Procedures Manual. National Computer Systems, Inc; Minneapolis, MN: 2000.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

