Subunit- and pathway-specific localization of NMDA receptors and scaffolding proteins at ganglion cell synapses in rat retina
- PMID: 19339621
- PMCID: PMC4283557
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5602-08.2009
Subunit- and pathway-specific localization of NMDA receptors and scaffolding proteins at ganglion cell synapses in rat retina
Abstract
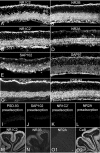
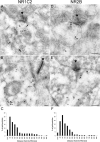
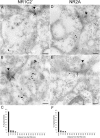
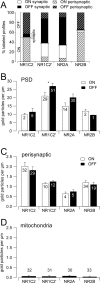
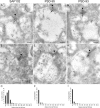
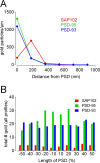
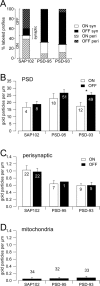
Retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) receive excitatory glutamatergic input from ON and OFF bipolar cells in distinct sublaminae of the inner plexiform layer (IPL). AMPA and NMDA receptors (AMPARs and NMDARs) mediate excitatory inputs in both synaptic layers, but specific roles for NMDARs at RGC synapses remain unclear. NMDARs comprise NR1 and NR2 subunits and are anchored by membrane-associated guanylate kinases (MAGUKs), but it is unknown whether particular NR2 subunits associate preferentially with particular NR1 splice variants and MAGUKs. Here, we used postembedding immunogold electron microscopy techniques to examine the subsynaptic localization of NMDAR subunits and MAGUKs at ON and OFF synapses onto rat RGCs. We found that the NR2A subunit, the NR1C2' splice variant, and MAGUKs PSD-95 and PSD-93 are localized to the postsynaptic density (PSD), preferentially at OFF synapses, whereas the NR2B subunit, the NR1C2 splice variant, and the MAGUK SAP102 are localized perisynaptically, with NR2B exhibiting a preference for ON synapses. Consistent with these anatomical data, spontaneous EPSCs (sEPSCs) recorded from OFF cells exhibited an NMDAR component that was insensitive to the NR2B antagonist Ro 25-6981. In ON cells, sEPSCs expressed an NMDAR component, partially sensitive to Ro 25-6981, only when glutamate transport was inhibited, indicating perisynaptic expression of NR2B NMDARs. These results provide the first evidence for preferential association of particular NR1 splice variants, NR2 subunits, and MAGUKs at central synapses and suggest that different NMDAR subtypes may play specific roles at functionally distinct synapses in the retinal circuitry.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Distinct perisynaptic and synaptic localization of NMDA and AMPA receptors on ganglion cells in rat retina.J Comp Neurol. 2006 Oct 20;498(6):810-20. doi: 10.1002/cne.21089. J Comp Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16927255 Free PMC article.
-
Coagonist release modulates NMDA receptor subtype contributions at synaptic inputs to retinal ganglion cells.J Neurosci. 2009 Feb 4;29(5):1469-79. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4240-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19193893 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptically released glutamate activates extrasynaptic NMDA receptors on cells in the ganglion cell layer of rat retina.J Neurosci. 2002 Mar 15;22(6):2165-73. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-06-02165.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11896156 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity and signal amplification of NMDA receptors.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006;18(1-2):71-84. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v18.i1-2.80. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 17725510 Review.
-
Regulation of neuronal PKA signaling through AKAP targeting dynamics.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;85(7):627-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.01.010. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16504338 Review.
Cited by
-
Spatial Organization and Dynamics of the Extracellular Space in the Mouse Retina.J Neurosci. 2020 Oct 7;40(41):7785-7794. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1717-20.2020. Epub 2020 Sep 4. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32887746 Free PMC article.
-
Melanopsin+RGCs Are fully Resistant to NMDA-Induced Excitotoxicity.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 20;20(12):3012. doi: 10.3390/ijms20123012. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31226772 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial organization of AMPAR subtypes in ON RGCs.J Neurosci. 2014 Jan 8;34(2):656-61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1140-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24403163 Free PMC article.
-
A synaptic signature for ON- and OFF-center parasol ganglion cells of the primate retina.Vis Neurosci. 2014 Jan;31(1):57-84. doi: 10.1017/S0952523813000461. Vis Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24801624 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of glycine-activated diheteromeric NR1/NR3 receptors in human embryonic kidney 293 cells Is NR1 splice variant-dependent.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009 Dec;331(3):975-84. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.158493. Epub 2009 Sep 2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009. PMID: 19726695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Hallaq RA, Yasuda RP, Wolfe BB. Enrichment of N-methyl-d-aspartate NR1 splice variants and synaptic proteins in rat postsynaptic densities. J Neurochem. 2001;77:110–119. - PubMed
-
- Amthor FR, Takahashi ES, Oyster CW. Morphologies of rabbit retinal ganglion cells with complex receptive fields. J Comp Neurol. 1989;280:97–121. - PubMed
-
- Andressen C, Blümcke I, Celio MR. Calcium-binding proteins: selective markers of nerve cells. Cell Tissue Res. 1993;271:181–208. - PubMed
-
- Aoki C, Miko I, Oviedo H, Mikeladze-Dvali T, Alexandre L, Sweeney N, Bredt DS. Electron microscopic immunocytochemical detection of PSD-95, PSD-93, SAP-102, and SAP-97 at postsynaptic, presynaptic, and nonsynaptic sites of adult and neonatal rat visual cortex. Synapse. 2001;40:239–257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
