Intravenous cyclophosphamide pulse therapy in the treatment of systemic sclerosis-related interstitial lung disease: a long term study
- PMID: 19340324
- PMCID: PMC2606648
- DOI: 10.2174/1874306400802010039
Intravenous cyclophosphamide pulse therapy in the treatment of systemic sclerosis-related interstitial lung disease: a long term study
Abstract
Objective: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) frequently complicates systemic sclerosis (SSc). Cyclophosphamide (CYC) is a promising immunosuppressive therapy for SSc-related ILD. Our objective was to investigate the effectiveness of an intravenous CYC (iv CYC) pulse regime in SSc-related ILD during treatment and thereafter.
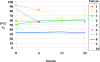
Methods: In a prospective observational study ten consecutive patients with SSc-related ILD were treated with iv CYC in a pulse regime lasting from 6 to 24 months. Clinical status, pulmonary functional testing (PFT) and high resolution computed tomography (HRCT) of the chest were evaluated at enrolment and 6, 12 and 24 months thereafter. After treatment withdrawal, patients were followed up every 6 months with PFT and chest HRCT to monitor lung disease.
Results: Clinical improvement was apparent in 8 out of 10 patients. The median values of forced vital capacity (FVC), forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1) and diffusion lung capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) as well as ground-glass pattern on HRCT did not change significantly after 6, 12 and 24 months of therapy. The follow-up continued in 8 out of 10 patients after treatment withdrawal for a median of 26.5 months (range: 12-48 months). The final median FVC was 54.5% of predicted value (interquartile range, IQR= 31.6%-94%). Only one patient suffered a FVC deterioration greater than 10%, even though less than 160 ml. The final median DLCO was 68% of predicted value (IQR=38.3-83.6%). Only 2 patients who developed pulmonary arterial hypertension deteriorated their DLCO values of more than 15%.
Conclusions: An iv CYC pulse regimen over 24 months may stabilize pulmonary activity in patients with SSc-related ILD during the course of treatment and for a median of 26.5 months thereafter.
Keywords: Systemic sclerosis; cyclophosphamide.; interstitial lung disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intravenous cyclophosphamide pulse therapy in interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis in a retrospective open-label study: influence of the extent of inflammation on pulmonary function.Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Oct;37(10):2715-2722. doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-4171-6. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Clin Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29987427 Free PMC article.
-
High-dose prednisolone and bolus cyclophosphamide in interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis: a prospective open study.Int J Rheum Dis. 2009 Sep;12(3):239-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1756-185X.2009.01417.x. Int J Rheum Dis. 2009. PMID: 20374353 Clinical Trial.
-
Cyclophosphamide pulse regimen in the treatment of alveolitis in systemic sclerosis.J Rheumatol. 2002 Apr;29(4):731-6. J Rheumatol. 2002. PMID: 11950014 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide in systemic sclerosis-related interstitial lung disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Aug;40(8):3185-3193. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-05794-5. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Clin Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 34080081
-
Serum concentration of surfactant protein D in patients with systemic sclerosis: The potential marker of the interstitial lung disease severity.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Aug;32(4):541-549. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2019.01.005. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 31174823 Review.
Cited by
-
Heterogeneity of determining disease severity, clinical course and outcomes in systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease: a systematic literature review.RMD Open. 2023 Nov;9(4):e003426. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003426. RMD Open. 2023. PMID: 37940340 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous Cyclophosphamide Therapy for Anti-IFN-Gamma Autoantibody-Associated Mycobacterium abscessus Infection.J Immunol Res. 2018 Dec 30;2018:6473629. doi: 10.1155/2018/6473629. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 30687765 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic sclerosis: comparison of efficacy of oral cyclophosphamide and azathioprine on skin score and pulmonary involvement-a retrospective study.Rheumatol Int. 2014 Dec;34(12):1691-9. doi: 10.1007/s00296-014-3026-y. Epub 2014 May 7. Rheumatol Int. 2014. PMID: 24801572
-
Long-term effects of immunosuppressive therapy on lung function in scleroderma patients.Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Nov;37(11):3043-3050. doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-4266-0. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Clin Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 30143960
-
Outcome of systemic sclerosis associated interstitial lung disease treated with intravenous cyclophosphamide.Clin Rheumatol. 2011 Aug;30(8):1099-104. doi: 10.1007/s10067-011-1734-1. Epub 2011 Apr 12. Clin Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21484227
References
-
- White B. Interstitial lung disease in scleroderma. Rheum Dis Clin N Am. 2003;29:371–390. - PubMed
-
- Jacobsen S, Ullman S, Shen GQ, et al. Influence of clinical features serum antinuclear antibodies, and lung function on survival of patients with systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 2001;28:2454–59. - PubMed
-
- Steen V, Medsger TA Jr. Severe organ involvement in systemic sclerosis with diffuse scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:2437–44. - PubMed
-
- Altman R, Medsger TA Jr, Bloch D, et al. Predictors of survival in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) Arthritis Rheum. 1991;34:403–13. - PubMed
-
- Hubbard R, Venn A. The impact of coexisting connective tissue disease on survival on patients with fibrosing alveolitis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2002;41:676–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources