Cell-cycle-based strategies to drive myocardial repair
- PMID: 19340478
- PMCID: PMC2691809
- DOI: 10.1007/s00246-009-9408-3
Cell-cycle-based strategies to drive myocardial repair
Abstract
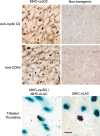
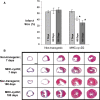
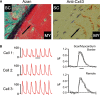
Cardiomyocytes exhibit robust proliferative activity during development. After birth, cardiomyocyte proliferation is markedly reduced. Consequently, regenerative growth in the postnatal heart via cardiomyocyte proliferation (and, by inference, proliferation of stem-cell-derived cardiomyocytes) is limited and often insufficient to affect repair following injury. Here, we review studies wherein cardiomyocyte cell cycle proliferation was induced via targeted expression of cyclin D2 in postnatal hearts. Cyclin D2 expression resulted in a greater than 500-fold increase in cell cycle activity in transgenic mice as compared to their nontransgenic siblings. Induced cell cycle activity resulted in infarct regression and concomitant improvement in cardiac hemodynamics following coronary artery occlusion. These studies support the notion that cell-cycle-based strategies can be exploited to drive myocardial repair following injury.
Figures
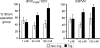
References
-
- Bergmann O, Bhardwaj RD, Bernard S, Zdunek S, Barnabé-Heider F, Walsh S, Zupicich J, Kanar Alkass, Buchholz BA, Druid H, Jovinge S, Frisen J (2008) Turnover of human cardiomyocytes. Circulation 118(Suppl):Abstract 3526
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

