Gene structures, biochemical characterization and distribution of rat melatonin receptors
- PMID: 19340560
- PMCID: PMC10717452
- DOI: 10.1007/s12576-008-0003-9
Gene structures, biochemical characterization and distribution of rat melatonin receptors
Abstract
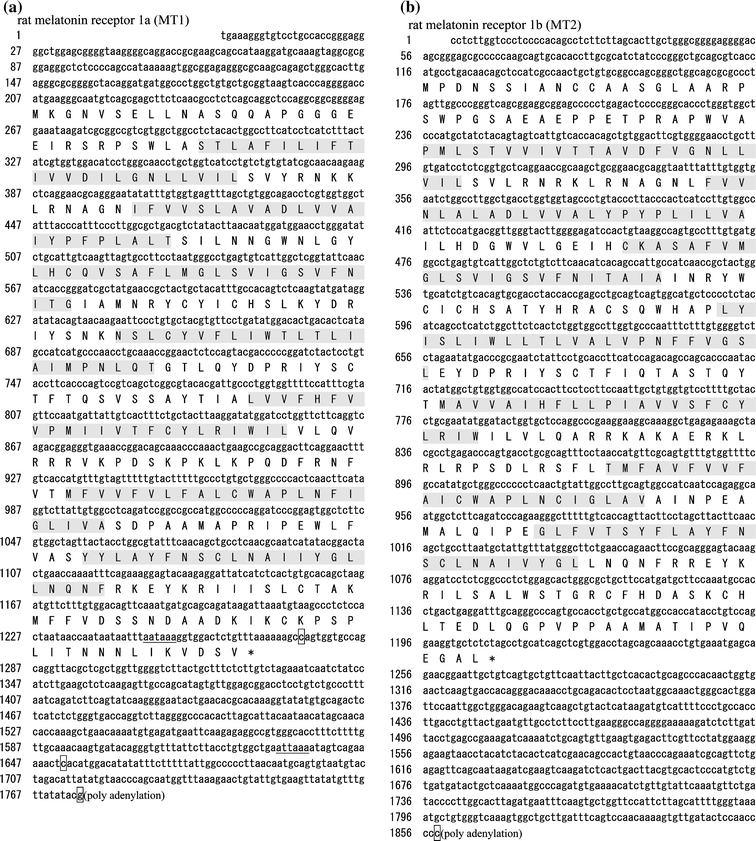
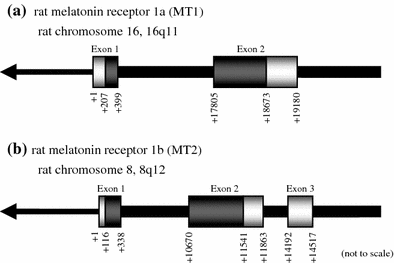
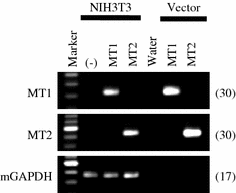
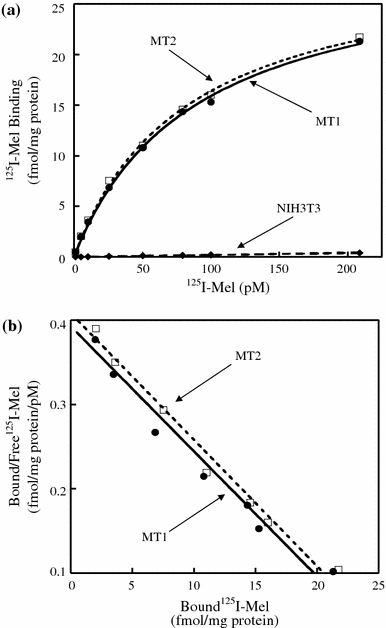
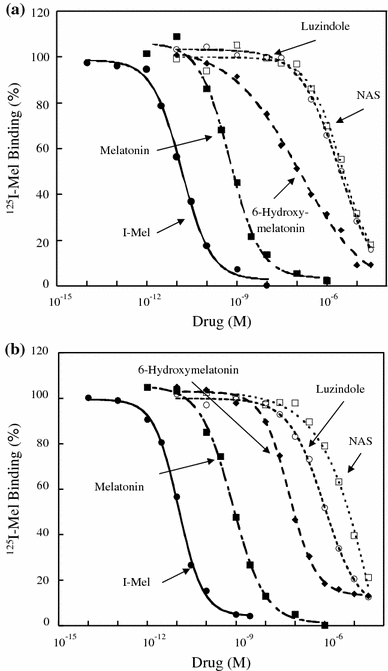
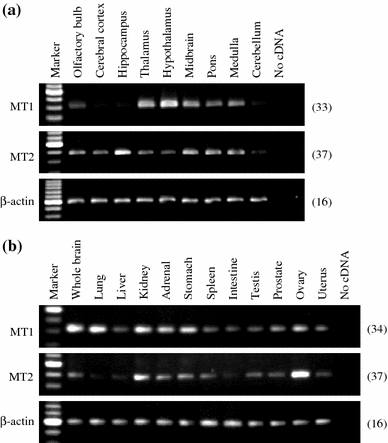
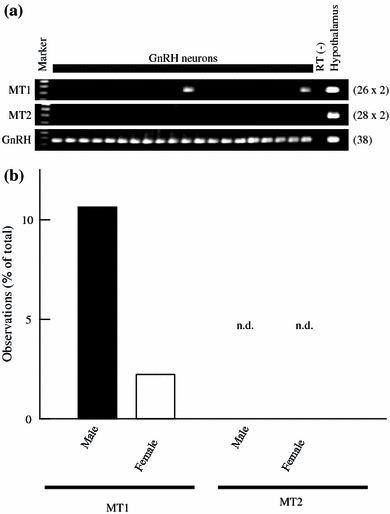
G-protein coupled receptors for the pineal hormone melatonin have been partially cloned from rats. However, insufficient information about their cDNA sequences has hindered studies of their distribution and physiological responses to melatonin using rats as an animal model. We have cloned cDNAs of two rat membrane melatonin receptor subtypes, melatonin receptor 1a (MT1) and melatonin receptor 1b (MT2), using a rapid amplification of cDNA end (RACE) method. The rat MT1 and MT2 cDNAs encode proteins of 353 and 364 amino acids, respectively, and show 78-93% identities with the human and mouse counterparts. Stable expression of either rat MT1 or MT2 in NIH3T3 cells resulted in high affinity 2-[(125)I]-iodomelatonin ((125)I-Mel) binding (K (d) = 73.2 +/- 9.0 and 73.7 +/- 2.9 pM, respectively), and exhibited a similar rank order of inhibition of specific (125)I-Mel binding by five ligands (2-iodomelatonin > melatonin > 6-hydroxymelatonin > luzindole > N-acetyl-5-hydroxytryptamine). RT-PCR analysis showed that MT1 is highly expressed in the hypothalamus, lung, kidney, adrenal gland, stomach, and ovary, while MT2 is highly expressed in the hippocampus, kidney, and ovary. We also performed multi-cell RT-PCR to examine the expression of mRNAs encoding MT1 and MT2 in adult GnRH neurons. MT1 was weakly expressed in male GnRH neurons, and was less expressed in the female neurons. MT2 expression was undetectable in GnRH neurons from either sex. This study delineates the gene structures, fundamental properties, and distribution of both rat melatonin receptor subtypes, and may offer opportunities to assess the physiological significance of melatonin in rats.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cetrorelix, a gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist, induces the expression of melatonin receptor 1a in the gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuronal cell line GT1-7.Neuroendocrinology. 2009;90(3):251-9. doi: 10.1159/000231993. Epub 2009 Jul 30. Neuroendocrinology. 2009. PMID: 19641296
-
Molecular cloning and pharmacological characterization of rat melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptors.Biochem Pharmacol. 2008 May 15;75(10):2007-19. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.02.022. Epub 2008 Mar 4. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18384758
-
Thirty-seven years of MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptor localization in the brain: Past and future challenges.J Pineal Res. 2024 Apr;76(3):e12955. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12955. J Pineal Res. 2024. PMID: 38606787 Review.
-
The end of a myth: cloning and characterization of the ovine melatonin MT(2) receptor.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Nov;158(5):1248-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00453.x. Epub 2009 Oct 8. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19814723 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin, Melatonin Receptors and Sleep: Moving Beyond Traditional Views.J Pineal Res. 2024 Oct;76(7):e13011. doi: 10.1111/jpi.13011. J Pineal Res. 2024. PMID: 39400423 Review.
Cited by
-
Olfaction and Melatonin: The Use of the Olfactory Discrimination Test.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2550:425-432. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2593-4_41. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36180710
-
Effects of Melatonin on Anterior Pituitary Plasticity: A Comparison Between Mammals and Teleosts.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jan 11;11:605111. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.605111. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33505357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic variant in HK1 is associated with a proanemic state and A1C but not other glycemic control-related traits.Diabetes. 2009 Nov;58(11):2687-97. doi: 10.2337/db09-0652. Epub 2009 Aug 3. Diabetes. 2009. PMID: 19651813 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian Rhythm Regulates Development of Enamel in Mouse Mandibular First Molar.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 5;11(8):e0159946. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159946. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27494172 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin in the mammalian olfactory bulb.Neuroscience. 2014 Mar 7;261:74-84. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.12.033. Epub 2013 Dec 21. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24365461 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

