Astrocyte- and endothelial-targeted CCL2 conditional knockout mice: critical tools for studying the pathogenesis of neuroinflammation
- PMID: 19340610
- PMCID: PMC2903863
- DOI: 10.1007/s12031-009-9197-4
Astrocyte- and endothelial-targeted CCL2 conditional knockout mice: critical tools for studying the pathogenesis of neuroinflammation
Abstract
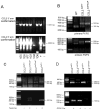
While the expression of the C-C chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) in the central nervous system (CNS) is associated with numerous neuroinflammatory conditions, the critical cellular sources of this chemokine, which is responsible for disease processes-as well as associated pathogenic mechanisms, remain unresolved. As the potential for anti-CCL2 therapeutics in treating neuroinflammatory disease is likely to be contingent upon effective drug delivery to the source(s) and/or target(s) of CCL2 action in the CNS, tools to highlight the course of CCL2 action during neuroinflammation are imperative. In response to this need, we used the Cre/loxP and FLP-FRT recombination system to develop the first two, cell-conditional CCL2 knockout mice-separately targeting CCL2 gene elimination to astrocytes and endothelial cells, both of which have been considered to play crucial though undefined roles in neuroinflammatory disease. Specifically, mice containing a floxed CCL2 allele were intercrossed with GFAP-Cre or Tie2-Cre transgenic mice to generate mice with CCL2-deficient astrocytes (astrocyte KO) or endothelial cells (endothelial KO), respectively. Polymerase chain reaction, reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction/quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of CCL2 gene, RNA, and protein, respectively, from cultured astrocytes and brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMEC) established the efficiency and specificity of the CCL2 gene deletions and a CCL2 null phenotype in these CNS cells. Effective cell-conditional knockout of CCL2 was also confirmed in an in vivo setting, wherein astrocytes and BMEC were retrieved by immune-guided laser capture microdissection from their in situ positions in the brains of mice experiencing acute, lipopolysaccharide-mediated endotoxemia to induce CCL2 gene expression. In vivo analysis further revealed apparent cross-talk between BMEC and astrocytes regarding the regulation of astrocyte CCL2 expression. Use of astrocyte KO and endothelial KO mice should prove critical in elaborating the pathogenic mechanisms of and optimizing the treatments for neuroinflammatory disease.
Figures




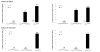

Similar articles
-
Astrocyte CCL2 sustains immune cell infiltration in chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Neuroimmunol. 2014 Sep 15;274(1-2):53-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2014.06.009. Epub 2014 Jun 24. J Neuroimmunol. 2014. PMID: 25005117 Free PMC article.
-
CCL2 modulates cytokine production in cultured mouse astrocytes.J Neuroinflammation. 2010 Oct 14;7:67. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-67. J Neuroinflammation. 2010. PMID: 20942978 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-selective knockout and 3D confocal image analysis reveals separate roles for astrocyte-and endothelial-derived CCL2 in neuroinflammation.J Neuroinflammation. 2014 Jan 21;11:10. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-11-10. J Neuroinflammation. 2014. PMID: 24444311 Free PMC article.
-
Altered hippocampal synaptic transmission in transgenic mice with astrocyte-targeted enhanced CCL2 expression.Brain Behav Immun. 2011 Jun;25 Suppl 1(0 1):S106-19. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2011.02.013. Epub 2011 Feb 26. Brain Behav Immun. 2011. PMID: 21356306 Free PMC article.
-
How inflammation modulates central nervous system vessel activation and provides targets for intervention--a personal perspective.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Oct;1207:1-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05785.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20955418 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Astrocyte CCL2 sustains immune cell infiltration in chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Neuroimmunol. 2014 Sep 15;274(1-2):53-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2014.06.009. Epub 2014 Jun 24. J Neuroimmunol. 2014. PMID: 25005117 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen mediates neuroprotection and anti-inflammatory effects during EAE through ERα signaling on astrocytes but not through ERβ signaling on astrocytes or neurons.J Neurosci. 2013 Jun 26;33(26):10924-33. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0886-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23804112 Free PMC article.
-
CCL2 modulates cytokine production in cultured mouse astrocytes.J Neuroinflammation. 2010 Oct 14;7:67. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-67. J Neuroinflammation. 2010. PMID: 20942978 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Causal Effect of Brain Expression of CCL2, NFKB1, MAPK14, TNFRSF1A, CXCL10 Genes on Multiple Sclerosis: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Approach.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 May 5;8:397. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00397. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32432099 Free PMC article.
-
Resolution of central nervous system astrocytic and endothelial sources of CCL2 gene expression during evolving neuroinflammation.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2014 Mar 4;11(1):6. doi: 10.1186/2045-8118-11-6. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2014. PMID: 24589378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott NJ. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:41–53. - PubMed
-
- Adamus G, Machnicki M, Amundson D, Adlard K, Offner H. Similar pattern of CCL2 expression in spinal cords and eyes of Lewis rats with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis associated anterior uveitis. J Neurosci Res. 1997;50:531–538. - PubMed
-
- Andjelkovic AV, Song L, Dzenko KA, Cong H, Pachter JS. Functional expression of CCR2 by human fetal astrocytes. J Neurosci Res. 2002;70:219–231. - PubMed
-
- Andjelkovic AV, Pachter JS. Characterization of MCP-1 and MIP-1α binding sites along human brain microvessels. J Neurochem. 2000;75:1898–1906. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

