Pentoxifylline versus prednisolone for severe alcoholic hepatitis: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 19340904
- PMCID: PMC2669113
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.15.1613
Pentoxifylline versus prednisolone for severe alcoholic hepatitis: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Aim: To compare the efficacy of pentoxifylline and prednisolone in the treatment of severe alcoholic hepatitis, and to evaluate the role of different liver function scores in predicting prognosis.
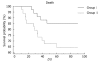
Methods: Sixty-eight patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis (Maddrey score > or = 32) received pentoxifylline (n = 34, group I) or prednisolone (n = 34, group II) for 28 d in a randomized double-blind controlled study, and subsequently in an open study (with a tapering dose of prednisolone) for a total of 3 mo, and were followed up over a period of 12 mo.
Results: Twelve patients in group II died at the end of 3 mo in contrast to five patients in group I. The probability of dying at the end of 3 mo was higher in group II as compared to group I (35.29% vs 14.71%, P = 0.04; log rank test). Six patients in group II developed hepatorenal syndrome as compared to none in group I. Pentoxifylline was associated with a significantly lower model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) score at the end of 28 d of therapy (15.53 +/- 3.63 vs 17.78 +/- 4.56, P = 0.04). Higher baseline Maddrey score was associated with increased mortality.
Conclusion: Reduced mortality, improved risk-benefit profile and renoprotective effects of pentoxifylline compared with prednisolone suggest that pentoxifylline is superior to prednisolone for treatment of severe alcoholic hepatitis.
Figures
Comment in
-
Pentoxifylline: a first line treatment option for severe alcoholic hepatitis and hepatorenal syndrome?World J Gastroenterol. 2009 Jul 7;15(25):3194-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3194. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19575503 Free PMC article.
-
Pentoxifylline and prednisolone in severe alcoholic hepatitis.Ann Hepatol. 2009 Oct-Dec;8(4):402-4. Ann Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 20009147 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lefkowitch JH. Morphology of alcoholic liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2005;9:37–53. - PubMed
-
- Teli MR, Day CP, Burt AD, Bennett MK, James OF. Determinants of progression to cirrhosis or fibrosis in pure alcoholic fatty liver. Lancet. 1995;346:987–990. - PubMed
-
- Perrot S, Beaugrand M. [Treatment of alcoholic hepatitis. A review of randomized trials] Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1988;12:521–531. - PubMed
-
- Stewart S, Jones D, Day CP. Alcoholic liver disease: new insights into mechanisms and preventative strategies. Trends Mol Med. 2001;7:408–413. - PubMed
-
- Zhang T, Li Y, Lai JP, Douglas SD, Metzger DS, O'Brien CP, Ho WZ. Alcohol potentiates hepatitis C virus replicon expression. Hepatology. 2003;38:57–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources