Passage of bone-marrow-derived liver stem cells in a proliferating culture system
- PMID: 19340907
- PMCID: PMC2669114
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.15.1630
Passage of bone-marrow-derived liver stem cells in a proliferating culture system
Abstract
Aim: To explore the feasibility of passage of bone-marrow-derived liver stem cells (BDLSCs) in culture systems that contain cholestatic serum.
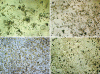
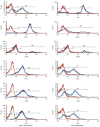
Methods: Whole bone marrow cells of rats were purified with conditioning selection media that contained 50 mL/L cholestatic serum. The selected BDLSCs were grown in a proliferating culture system and a differentiating culture system. The culture systems contained factors that stimulated the proliferation and differentiation of BDLSCs. Each passage of the proliferated stem cells was subjected to flow cytometry to detect stem cell markers. The morphology and phenotypic markers of BDLSCs were characterized using immunohistochemistry, reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and electron microscopy. The metabolic functions of differentiated cells were also determined by glycogen staining and urea assay.
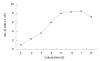
Results: The conditioning selection medium isolated BDLSCs directly from cultured bone marrow cells. The selected BDLSCs could be proliferated for six passages and maintained stable markers in our proliferating system. When the culture system was changed to a differentiating system, hepatocyte-like colony-forming units (H-CFUs) were formed. H-CFUs expressed markers of embryonic hepatocytes (alpha-fetoprotein, albumin and cytokeratin 8/18), biliary cells (cytokeratin 19), hepatocyte functional proteins (transthyretin and cytochrome P450-2b1), and hepatocyte nuclear factors 1alpha and -3beta). They also had glycogen storage and urea synthesis functions, two of the critical features of hepatocytes.
Conclusion: BDLSCs can be selected directly from bone marrow cells, and pure BDLSCs can be proliferated for six passages. The differentiated cells have hepatocyte-like phenotypes and functions. BDLSCs represent a new method to provide a readily available alternate source of cells for clinical hepatocyte therapy.
Figures

References
-
- Vieyra DS, Jackson KA, Goodell MA. Plasticity and tissue regenerative potential of bone marrow-derived cells. Stem Cell Rev. 2005;1:65–69. - PubMed
-
- Inagaki Y, Higashiyama R, Okazaki I. Treatment strategy for liver fibrosis through recruitment and differentiation of bone marrow stem/progenitor cells. Hepatol Res. 2007;37:991–993. - PubMed
-
- Banas A, Quinn G, Yamamoto Y, Teratani T, Ochiya T. “Stem cells into liver”--basic research and potential clinical applications. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006;585:3–17. - PubMed
-
- Thorgeirsson SS, Grisham JW. Hematopoietic cells as hepatocyte stem cells: a critical review of the evidence. Hepatology. 2006;43:2–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

