A combination treatment of entecavir and early-phase corticosteroid in severe exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B
- PMID: 19340912
- PMCID: PMC2669952
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.15.1650
A combination treatment of entecavir and early-phase corticosteroid in severe exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B
Abstract
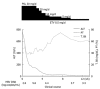
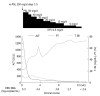
Of patients with severe exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B accompanied by jaundice and coagulopathy, 20%-30% have a fatal outcome. In this report, we describe 2 cases of severe exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B with jaundice and coagulopathy who were successfully treated with a combination of entecavir and corticosteroid. In both cases, rapid reductions in serum hepatitis B virus (HBV)-DNA levels were observed, and corticosteroid was stopped after serum HBV-DNA levels became undetectable. Entecavir treatment was continued. Generally, entecavir treatment reduced serum HBV-DNA levels rapidly, although the improvement in liver function was delayed by a few weeks. During this time lag, liver cell injury continued and the disease progressed. Corticosteroid suppressed the excessive host immune response and was useful for stopping progressive deterioration. A combination of entecavir and early-phase corticosteroid may be a useful treatment in severe exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early hepatitis B virus DNA reduction in hepatitis B e antigen-positive patients with chronic hepatitis B: A randomized international study of entecavir versus adefovir.Hepatology. 2009 Jan;49(1):72-9. doi: 10.1002/hep.22658. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19065670 Clinical Trial.
-
Persistent Loss of Hepatitis B Virus Markers in Serum without Cellular Immunity by Combination of Peginterferon and Entecavir Therapy in Humanized Mice.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Aug 24;61(9):e00725-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00725-17. Print 2017 Sep. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28696237 Free PMC article.
-
A 24-week, parallel-group, open-label, randomized clinical trial comparing the early antiviral efficacy of telbivudine and entecavir in the treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B virus infection in adult Chinese patients.Clin Ther. 2010 Apr;32(4):649-58. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.04.001. Clin Ther. 2010. PMID: 20435234 Clinical Trial.
-
Three years of continuous entecavir therapy in treatment-naïve chronic hepatitis B patients: VIRAL suppression, viral resistance, and clinical safety.Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 Jul;106(7):1264-71. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2011.45. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21364549
-
Entecavir for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection.Clin Ther. 2006 Feb;28(2):184-203. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2006.02.012. Clin Ther. 2006. PMID: 16678641 Review.
Cited by
-
SOCS3 and IL-6 mRNA levels in PBMC enhance the early prediction for patients with acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure receiving glucocorticoid therapy.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jun 5;15:1571443. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1571443. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40538651 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of Nucleos(t)ide analogues in patients with spontaneous acute exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 11;8(6):e65952. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065952. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23776577 Free PMC article.
-
The requirement for a sufficient period of corticosteroid treatment in combination with nucleoside analogue for severe acute exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B.J Gastroenterol. 2010 Dec;45(12):1255-62. doi: 10.1007/s00535-010-0280-y. Epub 2010 Jul 9. J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20614156 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Tenofovir Combined with Recombinant Human Interferon α-2b on Negative Conversion Rate, Liver Function, Immune Status, and Drug Safety in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jun 30;2022:1889628. doi: 10.1155/2022/1889628. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Nov 29;2022:9791408. doi: 10.1155/2022/9791408. PMID: 35815265 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Plasma Interleukin-10: A Likely Predictive Marker for Hepatitis B Virus-Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure.Hepat Mon. 2014 Jul 14;14(7):e19370. doi: 10.5812/hepatmon.19370. eCollection 2014 Jul. Hepat Mon. 2014. PMID: 25147572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Papatheodoridis GV, Manolakopoulos S, Dusheiko G, Archimandritis AJ. Therapeutic strategies in the management of patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2008;8:167–178. - PubMed
-
- Perrillo RP. Acute flares in chronic hepatitis B: the natural and unnatural history of an immunologically mediated liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2001;120:1009–1022. - PubMed
-
- Seeff LB, Koff RS. Evolving concepts of the clinical and serologic consequences of hepatitis B virus infection. Semin Liver Dis. 1986;6:11–22. - PubMed
-
- Tsubota A, Arase Y, Suzuki Y, Suzuki F, Sezaki H, Hosaka T, Akuta N, Someya T, Kobayashi M, Saitoh S, et al. Lamivudine monotherapy for spontaneous severe acute exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;20:426–432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

