Hand2 is required in the epithelium for palatogenesis in mice
- PMID: 19341725
- PMCID: PMC2745957
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.03.021
Hand2 is required in the epithelium for palatogenesis in mice
Abstract
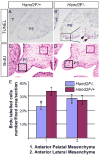
The basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor Hand2 has been implicated in the development of multiple organs, including craniofacial organs. Mice carrying Hand2 hypomorphic alleles (Hand2(LoxP/-)) display a cleft palate phenotype. A specific deletion of the Hand2 branchial arch-specific enhancer also leads to a hypoplastic mandible and cleft palate formation in mice. However, the underlying mechanism of Hand2 regulation of palate development remains unknown. Here we show that Hand2 is expressed in both the epithelium and mesenchyme of the developing palate. While mesenchymal specific inactivation of Hand2 has no impact on palate development, epithelial specific deletion of Hand2 creates a cleft palate phenotype. Hand2 appears to exert distinct roles in the anterior and posterior palate. In the anterior palate of Hand2(LoxP/-) mice, premature death of periderm cells and a down-regulation of Shh are observed in the medial edge epithelium (MEE), accompanied by a decreased level of cell proliferation in the palatal mesenchyme. In the posterior palate, a lower dose of Hand2 causes aberrant periderm cell death on the surface of the epithelium, triggering abnormal fusion between the palatal shelf and mandible and preventing palatal shelf elevation. We further demonstrate that BMP activities are essential for the expression of Hand2 in the palate. We conclude that Hand2 is an intrinsic regulator in the epithelium and is required for palate development.
Figures







References
-
- Alappat SR, Zhang Z, Suzuki K, Zhang X, Liu H, Jiang R, Yamada G, Chen YP. The cellular and molecular etiology of the cleft secondary palate in Fgf10 mutant mice. Dev Biol. 2005;277:102–113. - PubMed
-
- Chai Y, Jiang X, Ito Y, Bringas P, Han J, Rowitch DH, Soriano P, McMahon AP, Sucov HM. Fate of the mammalian cranial neural crest during tooth and mandibular morphogenesis. Development. 2000;127:1671–1679. - PubMed
-
- Charite J, McFadden DG, Olson EN. The bHLH transcription factor dHAND controls Sonic hedgehog expression and establishment of the zone of polarizing activity during limb development. Development. 2000;127:2461–2470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

