Structural basis for the activation of muscle contraction by troponin and tropomyosin
- PMID: 19341744
- PMCID: PMC2693027
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.03.060
Structural basis for the activation of muscle contraction by troponin and tropomyosin
Abstract
The molecular regulation of striated muscle contraction couples the binding and dissociation of Ca(2+) on troponin (Tn) to the movement of tropomyosin on actin filaments. In turn, this process exposes or blocks myosin binding sites on actin, thereby controlling myosin crossbridge dynamics and consequently muscle contraction. Using 3D electron microscopy, we recently provided structural evidence that a C-terminal extension of TnI is anchored on actin at low Ca(2+) and competes with tropomyosin for a common site to drive tropomyosin to the B-state location, a constrained, relaxing position on actin that inhibits myosin-crossbridge association. Here, we show that release of this constraint at high Ca(2+) allows a second segment of troponin, probably representing parts of TnT or the troponin core domain, to promote tropomyosin movement on actin to the Ca(2+)-induced C-state location. With tropomyosin stabilized in this position, myosin binding interactions can begin. Tropomyosin appears to oscillate to a higher degree between respective B- and C-state positions on troponin-free filaments than on fully regulated filaments, suggesting that tropomyosin positioning in both states is troponin-dependent. By biasing tropomyosin to either of these two positions, troponin appears to have two distinct structural functions; in relaxed muscles at low Ca(2+), troponin operates as an inhibitor, while in activated muscles at high Ca(2+), it acts as a promoter to initiate contraction.
Figures
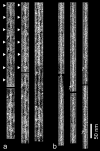
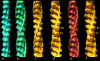
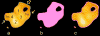

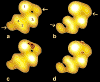
References
-
- Gordon AM, Homsher E, Regnier M. Regulation of contraction in striated muscle. Physiol Rev. 2000;80:853–924. - PubMed
-
- Tobacman LS. Thin filament-mediated regulation of cardiac contraction. Annu Rev Physiol. 1996;58:447–481. - PubMed
-
- Moore PB, Huxley HE, DeRosier DJ. Three-dimensional reconstruction of F-actin, thin filaments and decorated thin filaments. J Mol Biol. 1970;50:279–292. - PubMed
-
- O’Brien EJ, Bennett PM, Hanson J. Optical diffraction studies of myofibrillar structure. Philos Trans Roy Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971;261:201–208. - PubMed
-
- Spudich JA, Huxley HE, Finch JT. The regulation of skeletal muscle contraction. II Structural studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin. J Mol Biol. 1972;72:619–632. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

