Epidermal growth factor activates Na(+/)H(+) exchanger in podocytes through a mechanism that involves Janus kinase and calmodulin
- PMID: 19341767
- PMCID: PMC3364543
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2009.03.006
Epidermal growth factor activates Na(+/)H(+) exchanger in podocytes through a mechanism that involves Janus kinase and calmodulin
Abstract
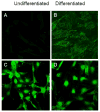
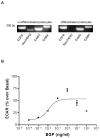
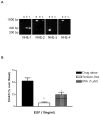
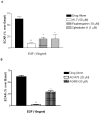
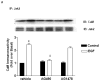
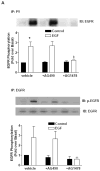
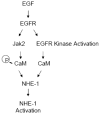
Sodium-proton exchanger type 1 (NHE-1) is ubiquitously expressed, is activated by numerous growth factors, and plays significant roles in regulating intracellular pH and cellular volume, proliferation and cytoskeleton. Despite its importance, little is known about its regulation in renal glomerular podocytes. In the current work, we studied the regulation of NHE-1 activity by the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in cultured podocytes. RT-PCR demonstrated mRNAs for NHE-1 and NHE-2 in differentiated podocytes, as well as for EGFR subunits EGFR/ErbB1, Erb3, and ErbB4. EGF induced concentration-dependent increases in proton efflux in renal podocytes as assessed using a Cytosensor microphysiometer, were diminished in the presence of 5-(N-methyl-N-isobutyl) amiloride or in a sodium-free solution. Furthermore, pharmacological inhibitors of Janus kinase (Jak2) and calmodulin (CaM) attenuated EGF-induced NHE-1 activity. Co-immunoprecipitation studies determined that EGF induced formation of complexes between Jak2 and CaM, as well as between CaM and NHE-1. In addition, EGF increased levels of tyrosine phosphorylation of Jak2 and CaM. The EGFR kinase inhibitor, AG1478, blocked activation of NHE-1, but did not block EGF-induced phosphorylation of Jak2 or CaM. These results suggest that EGF induces NHE-1 activity in podocytes through two pathways: (1) EGF-->EGFR-->Jak2 activation (independent of EGFR tyrosine kinase activity)-->tyrosine phosphorylation of CaM-->CaM binding to NHE-1-->conformational change of NHE-1-->activation of NHE-1; and (2) EGF-->EGFR-->EGFR kinase activation-->association of CaM with NHE-1 (independent of Jak2)-->conformational change of NHE-1-->activation of NHE-1.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epidermal growth factor-induced proliferation of collecting duct cells from Oak Ridge polycystic kidney mice involves activation of Na+/H+ exchanger.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014 Sep 15;307(6):C554-60. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00188.2014. Epub 2014 Jul 23. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25055824 Free PMC article.
-
Hypertonicity activates Na+/H+ exchange through Janus kinase 2 and calmodulin.J Biol Chem. 2003 May 9;278(19):16908-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209883200. Epub 2003 Mar 7. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12626508
-
Bradykinin B2 receptors activate Na+/H+ exchange in mIMCD-3 cells via Janus kinase 2 and Ca2+/calmodulin.J Biol Chem. 2001 May 18;276(20):17339-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M010834200. Epub 2001 Feb 16. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11278760
-
Growth hormone-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of EGF receptor as an essential element leading to MAP kinase activation and gene expression.Endocr J. 1998 Apr;45 Suppl:S27-31. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.45.suppl_s27. Endocr J. 1998. PMID: 9790226 Review.
-
The links between cellular Ca2+ and Na+/H+ exchange in the pathophysiology of essential hypertension.Am J Hypertens. 1996 Jul;9(7):703-7. doi: 10.1016/0895-7061(95)00447-5. Am J Hypertens. 1996. PMID: 8806985 Review.
Cited by
-
The Na+ /H+ exchanger NHE1 localizes as clusters to cryptic lamellipodia and accelerates collective epithelial cell migration.J Physiol. 2019 Feb;597(3):849-867. doi: 10.1113/JP277383. Epub 2018 Dec 17. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30471113 Free PMC article.
-
Lysosome trafficking is necessary for EGF-driven invasion and is regulated by p38 MAPK and Na+/H+ exchangers.BMC Cancer. 2017 Oct 4;17(1):672. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3660-3. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28978320 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Na⁺/H⁺ exchanger type 1 and intracellular pH in angiotensin II-induced reactive oxygen species generation and podocyte apoptosis.J Pharmacol Sci. 2013;122(3):176-83. doi: 10.1254/jphs.12291fp. Epub 2013 Jun 22. J Pharmacol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23800993 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor-induced proliferation of collecting duct cells from Oak Ridge polycystic kidney mice involves activation of Na+/H+ exchanger.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014 Sep 15;307(6):C554-60. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00188.2014. Epub 2014 Jul 23. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25055824 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of miR-146a in Podocytes Increases Risk of Diabetic Glomerulopathy via Up-regulation of ErbB4 and Notch-1.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jan 13;292(2):732-747. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.753822. Epub 2016 Dec 2. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 27913625 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nowak G, Schnellmann RG. Integrative effects of EGF on metabolism and proliferation in renal proximal tubular cells. Am J Physiol. 1995;269:C1317–1325. - PubMed
-
- Schaudies RP, Nonclercq D, Nelson L, Toubeau G, Zanen J, Heuson-Stiennon JA, Laurent G. Endogenous EGF as a potential renotrophic factor in ischemia-induced acute renal failure. Am J Physiol. 1993;265:F425–434. - PubMed
-
- Sakurai H, Tsukamoto T, Kjelsberg CA, Cantley LG, Nigam SK. EGF receptor ligands are a large fraction of in vitro branching morphogens secreted by embryonic kidney. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:F463–472. - PubMed
-
- Fleck C, Pertsch J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) increases the renal amino acid transport capacity in amino acid loaded rats. Amino Acids. 1998;15:307–320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

