Tumor detection and elimination by a targeted gallium corrole
- PMID: 19342490
- PMCID: PMC2669340
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0901531106
Tumor detection and elimination by a targeted gallium corrole
Abstract
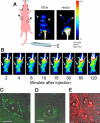
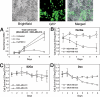
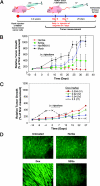
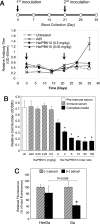
Sulfonated gallium(III) corroles are intensely fluorescent macrocyclic compounds that spontaneously assemble with carrier proteins to undergo cell entry. We report in vivo imaging and therapeutic efficacy of a tumor-targeted corrole noncovalently assembled with a heregulin-modified protein directed at the human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER). Systemic delivery of this protein-corrole complex results in tumor accumulation, which can be visualized in vivo owing to intensely red corrole fluorescence. Targeted delivery in vivo leads to tumor cell death while normal tissue is spared. These findings contrast with the effects of doxorubicin, which can elicit cardiac damage during therapy and required direct intratumoral injection to yield similar levels of tumor shrinkage compared with the systemically delivered corrole. The targeted complex ablated tumors at >5 times a lower dose than untargeted systemic doxorubicin, and the corrole did not damage heart tissue. Complexes remained intact in serum and the carrier protein elicited no detectable immunogenicity. The sulfonated gallium(III) corrole functions both for tumor detection and intervention with safety and targeting advantages over standard chemotherapeutic agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kawasaki ES, Player A. Nanotechnology, nanomedicine, and the development of new, effective therapies for cancer. Nanomedicine. 2005;1:101–109. - PubMed
-
- Chowdhary RK, et al. Correlation of photosensitizer delivery to lipoproteins and efficacy in tumor and arthritis mouse models; comparison of lipid-based and Pluronic P123 formulations. J Pharm Sci. 2003;6:198–204. - PubMed
-
- Haber A, et al. Amphiphilic/bipolar metallocorroles that catalyze the decomposition of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, rescue lipoproteins from oxidative damage, and attenuate atherosclerosis in mice. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2008;16:16. - PubMed
-
- Mahammed A, Gray HB, Weaver JJ, Sorasaenee K, Gross Z. Amphiphilic corroles bind tightly to human serum albumin. Bioconjugate Chem. 2004;15:738–746. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

