Role of iron in the pathogenesis of cysteamine-induced duodenal ulceration in rats
- PMID: 19342511
- PMCID: PMC3834006
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.90257.2008
Role of iron in the pathogenesis of cysteamine-induced duodenal ulceration in rats
Abstract
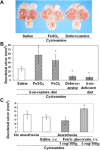
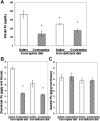
Cysteamine induces perforating duodenal ulcers in rats within 24-48 h. This reducing aminothiol generates hydrogen peroxide in the presence of transition metals (e.g., ferric iron), producing oxidative stress, which may contribute to organ-specific tissue damage. Since most intestinal iron absorption takes place in the proximal duodenum, we hypothesized that cysteamine may disrupt regulation of mucosal iron transport, and iron may facilitate cysteamine-induced duodenal ulceration. We show here that cysteamine-induced ulceration was aggravated by pretreatment of rats with Fe(3+) or Fe(2+) compounds, which elevated iron concentration in the duodenal mucosa. In contrast, feeding rats an iron-deficient diet was associated with a 4.6-fold decrease in ulcer formation, accompanied by a 34% decrease (P < 0.05) in the duodenal mucosal iron concentration. Administration of deferoxamine inhibited ulceration by 65%. We also observed that the antiulcer effect of H2 receptor antagonist cimetidine included a 35% decrease in iron concentration in the duodenal mucosa. Cysteamine-induced duodenal ulcers were also decreased in iron-deficient Belgrade rats (P < 0.05). In normal rats, cysteamine administration increased the iron concentration in the proximal duodenal mucosa by 33% in the preulcerogenic stage but at the same time decreased serum iron (P < 0.05). Cysteamine also enhanced activation of mucosal iron regulatory protein 1 and increased the expression of divalent metal transporter 1 mRNA and protein. Transferrin receptor 1 protein expression was also increased, although mucosal ferroportin and ferritin remained almost unchanged. These results indicate an expansion of the intracellular labile iron pool in the duodenal mucosa, increasing its susceptibility to oxidative stress, and suggest a role for iron in the pathogenesis of organ-specific tissue injury such as duodenal ulcers.
Figures






Similar articles
-
New mechanistic explanation for the localization of ulcers in the rat duodenum: role of iron and selective uptake of cysteamine.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012 Sep 1;525(1):60-70. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2012.05.013. Epub 2012 Jun 7. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012. PMID: 22684023
-
Mucosal enzyme activities, with special reference to enzymes implicated in bicarbonate secretion, in the duodenum of rats with cysteamine-induced ulcers.Clin Sci (Lond). 1983 Mar;64(3):341-7. doi: 10.1042/cs0640341. Clin Sci (Lond). 1983. PMID: 6822066
-
Cysteamine-induced inhibition of mucosal and pancreatic alkaline secretion in rat duodenum.Dig Dis Sci. 1988 Mar;33(3):330-7. doi: 10.1007/BF01535759. Dig Dis Sci. 1988. PMID: 3342725
-
From cysteamine to MPTP: structure-activity studies with duodenal ulcerogens.Toxicol Pathol. 1988;16(2):205-12. doi: 10.1177/019262338801600213. Toxicol Pathol. 1988. PMID: 3055230 Review.
-
From Selye's and Szabo's Cysteamine-Duodenal Ulcer in Rats to Dopamine in the Stomach: Therapy Significance and Possibilities.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Dec 7;16(12):1699. doi: 10.3390/ph16121699. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38139825 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ghrelin accelerates the healing of cysteamine-induced duodenal ulcers in rats.Med Sci Monit. 2012 May;18(5):BR181-7. doi: 10.12659/msm.882727. Med Sci Monit. 2012. PMID: 22534700 Free PMC article.
-
STAT3 and importins are novel mediators of early molecular and cellular responses in experimental duodenal ulceration.Dig Dis Sci. 2014 Feb;59(2):297-306. doi: 10.1007/s10620-013-2807-6. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Dig Dis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24385009
-
Measurement of Trace Elements (Zinc, Copper, Magnesium, and Iron) in the Saliva of Horses: Validation Data and Changes in Equine Gastric Ulcer Syndrome (EGUS).Animals (Basel). 2024 Jun 7;14(12):1724. doi: 10.3390/ani14121724. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929343 Free PMC article.
-
Stable isotope gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry determination of aminoethylcysteine ketimine decarboxylated dimer in biological samples.Anal Biochem. 2012 Nov 1;430(1):4-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2012.07.022. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Anal Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22858756 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrointestinal challenges in nephropathic cystinosis: clinical perspectives.Pediatr Nephrol. 2024 Oct;39(10):2845-2860. doi: 10.1007/s00467-023-06211-6. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Pediatr Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38393360 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adamama-Moraitou K, Rallis T, Papasteriadis A, Roubies N, Kaldrimidou H. Iron, zinc, and copper concentration in serum, various organs, and hair of dogs with experimentally induced exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Dig Dis Sci 46: 1444–1457, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Adler RS, Gallagher GT, Szabo S. Duodenal ulcerogens cysteamine and propionitrile decrease duodenal neutralization of acid in the rat. Dig Dis Sci 288: 716–723, 1983 - PubMed
-
- Anderson GJ, Vulpe CD. Regulation of intestinal iron transport. In: Molecular and Cellular Iron Transport, edited by D. Templeton New York: Marcel Dekker, 2001, pp. 559–596.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

