Amplification of coronary arteriogenic capacity of multipotent stromal cells by epidermal growth factor
- PMID: 19342596
- PMCID: PMC2796538
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.186189
Amplification of coronary arteriogenic capacity of multipotent stromal cells by epidermal growth factor
Abstract
Objective: We determined whether increasing adherence of multipotent stromal cells (MSCs) would amplify their effects on coronary collateral growth (CCG).
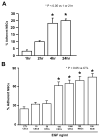
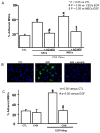
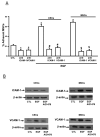
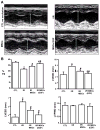
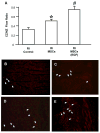
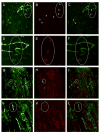
Methods and results: Adhesion was established in cultured coronary endothelials cells (CECs) or MSCs treated with epidermal growth factor (EGF). EGF increased MSCs adhesion to CECs, and increased intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM-1) or vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM-1) expression. Increased adherence was blocked by EGF receptor antagonism or antibodies to the adhesion molecules. To determine whether adherent MSCs, treated with EGF, would augment CCG, repetitive episodes of myocardial ischemia (RI) were introduced and CCG was measured from the ratio of collateral-dependent (CZ) and normal zone (NZ) flows. CZ/NZ was increased by MSCs without treatment versus RI-control and was further increased by EGF-treated MSCs. EGF-treated MSCs significantly improved myocardial function versus RI or RI+MSCs demonstrating that the increase in collateral flow was functionally significant. Engraftment of MSCs into myocardium was also increased by EGF treatment.
Conclusions: These results reveal the importance of EGF in MSCs adhesion to endothelium and suggest that MSCs may be effective therapies for the stimulation of coronary collateral growth when interventions are used to increase their adhesion and homing (in vitro EGF treatment) to the jeopardized myocardium.
Figures
References
-
- Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT, Murray CJ. Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: systematic analysis of population health data. Lancet. 2006;367:1747–1757. - PubMed
-
- Vismara LA, Miller RR, Price JE, Karem R, DeMaria AN, Mason DT. Improved longevity due to reduction of sudden death by aortocoronary bypass in coronary atherosclerosis. Am J Cardiol. 1977;39:919–924. - PubMed
-
- Holmes DR, Jr, Kim LJ, Brooks MM, Kip KE, Schaff HV, Detre KM, Frye RL. The effect of coronary artery bypass grafting on specific causes of long-term mortality in the Bypass Angioplasty Revascularization Investigation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;134:38–46. 46 e31. - PubMed
-
- Minguell JJ, Erices A. Mesenchymal stem cells and the treatment of cardiac disease. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2006;231:39–49. - PubMed
-
- Mangi AA, Noiseux N, Kong D, He H, Rezvani M, Ingwall JS, Dzau VJ. Mesenchymal stem cells modified with Akt prevent remodeling and restore performance of infarcted hearts. Nat Med. 2003;9:1195–1201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

