Statins impair CD1d-mediated antigen presentation through the inhibition of prenylation
- PMID: 19342651
- PMCID: PMC2850571
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0804311
Statins impair CD1d-mediated antigen presentation through the inhibition of prenylation
Abstract
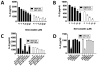
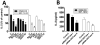
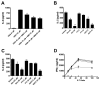
Statins are widely used as cholesterol-lowering agents that also decrease inflammation and target enzymes essential for prenylation, an important process in the activation and intracellular transport of proteins vital for a wide variety of cellular functions. Here, we report that statins impair a critical component of the innate immune response, CD1d-mediated Ag presentation. The addition of specific intermediates in the isoprenylation pathway reversed this effect, whereas specific targeting of enzymes responsible for prenylation mimicked the inhibitory effects of statins on Ag presentation by CD1d as well as MHC class II molecules. This study demonstrates the importance of isoprenylation in the regulation of Ag presentation and suggests a mechanism by which statins reduce inflammatory responses.
Figures



References
-
- Goldstein JL, Brown MS. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990;343:425–430. - PubMed
-
- Arnaud C, Veillard NR, Mach F. Cholesterol-independent effects of statins in inflammation, immunomodulation and atherosclerosis. Curr. Drug Targets. 2005;5:127–134. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein MR, Mascitelli L, Pezzetta F. The double-edged sword of statin immunomodulation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2008 In Press. - PubMed
-
- Wierzbicki AS, Poston R, Ferro A. The lipid and non-lipid effects of statins. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003;99:95–112. - PubMed
-
- Yoshida M. Potential role of statins in inflammation and atherosclerosis. J. Atheroscl. Thromb. 2003;10:140–144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

