Requisite role for the dectin-1 beta-glucan receptor in pulmonary defense against Aspergillus fumigatus
- PMID: 19342673
- PMCID: PMC3434356
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0804250
Requisite role for the dectin-1 beta-glucan receptor in pulmonary defense against Aspergillus fumigatus
Abstract
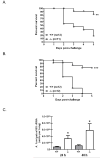
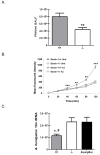
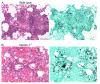
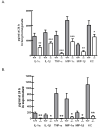
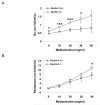
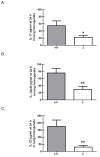
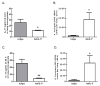
Immune suppression increases the incidence of invasive fungal infections, particularly those caused by the opportunistic mold Aspergillus fumigatus. Previous investigations revealed that members of the TLR family are not absolutely required for host defense against A. fumigatus in nonimmunosuppressed hosts, suggesting that other pattern recognition receptors are involved. We show in this study that naive mice (i.e., not pharmacologically immunosuppressed) lacking the beta-glucan receptor Dectin-1 (Dectin-1(-/-)) are more sensitive to intratracheal challenge with A. fumigatus than control mice, exhibiting >80% mortality within 5 days, ultimately attributed to a compromise in respiratory mechanics. In response to A. fumigatus challenge, Dectin-1(-/-) mice demonstrated impaired IL-1alpha, IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, CCL3/MIP-1alpha, CCL4/MIP-1beta, and CXCL1/KC production, which resulted in insufficient lung neutrophil recruitment and uncontrolled A. fumigatus lung growth. Alveolar macrophages from Dectin-1(-/-) mice failed to produce proinflammatory mediators in response to A. fumigatus, whereas neutrophils from Dectin-1(-/-) mice had impaired reactive oxygen species production and impaired killing of A. fumigatus. We further show that IL-17 production in the lung after A. fumigatus challenge was Dectin-1 dependent, and that neutralization of IL-17 significantly impaired A. fumigatus clearance. Collectively, these results support a requisite role for Dectin-1 in in vivo defense against A. fumigatus.
Figures
References
-
- Marr KA, Patterson T, Denning D. Aspergillosis pathogenesis, clinical manifestations and therapy. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2002;16:875–894. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PD, Marr KA. Risks, diagnosis and outcomes of invasive fungal infections in haematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Brit J Haematol. 2007;139:519–531. - PubMed
-
- Fukuda T, Boeckh M, Carter RA, Sandmaier BM, Maris MB, Maloney DG, Martin PJ, Storb RF, Marr KA. Risks and outcomes of invasive fungal infections in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplants after nonmyeloablative conditioning. Blood. 2003;102:827–833. - PubMed
-
- Perlroth J, Choi B, Spellberg B. Nosocomial fungal infections: epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment. Med Mycol. 2007;45:321–346. - PubMed
-
- Bulpa P, Dive A, Sibille Y. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Resp J. 2007;30:782–800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

