Recommendations for management of dyslipidemia in high cardiovascular risk patients
- PMID: 19343119
- PMCID: PMC2586399
Recommendations for management of dyslipidemia in high cardiovascular risk patients
Abstract
Overwhelming evidence supports a causal relationship between elevated levels of plasma cholesterol, particularly low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and increased risk of coronary artery disease, which remains the leading cause of death and morbidity worldwide. Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol lowering has been the main goal of therapy, and clinical trial results from recently published studies of intensive statin therapy confirm the benefits of more aggressive lipid-lowering targets, particularly in subjects at high risk for cardiovascular events. This management update will focus on the implications of risk reduction in patients at high cardiovascular risk, and will provide practical steps to help further risk stratify these patients and help them reach their target goals.
Keywords: Coronary artery disease; Dyslipidemia; LDL cholesterol; Treatment.
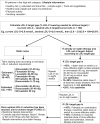
Figures

Similar articles
-
AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGISTS AND AMERICAN COLLEGE OF ENDOCRINOLOGY GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF DYSLIPIDEMIA AND PREVENTION OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE.Endocr Pract. 2017 Apr;23(Suppl 2):1-87. doi: 10.4158/EP171764.APPGL. Endocr Pract. 2017. PMID: 28437620
-
Lowering Targeted Atherogenic Lipoprotein Cholesterol Goals for Patients at "Extreme" ASCVD Risk.Curr Diab Rep. 2019 Nov 21;19(12):146. doi: 10.1007/s11892-019-1246-y. Curr Diab Rep. 2019. PMID: 31754844 Review.
-
Perspectives on low-density lipoprotein cholesterol goal achievement.Curr Med Res Opin. 2009 Feb;25(2):431-47. doi: 10.1185/03007990802631438. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009. PMID: 19192988 Review.
-
Vascular Quality of Care Assessment: Clinicians' Adherence to Lipid-Lowering Therapy for Patients with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease.Ann Vasc Surg. 2020 Nov;69:197-205. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2020.06.003. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Ann Vasc Surg. 2020. PMID: 32554202
-
Residual dyslipidemia according to low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and apolipoprotein B among statin-treated US adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009-2010.J Clin Lipidol. 2015 Jul-Aug;9(4):525-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2015.05.003. Epub 2015 May 16. J Clin Lipidol. 2015. PMID: 26228670
Cited by
-
Understanding gender differences in statin use among elderly Medicare beneficiaries: an application of decomposition technique.Drugs Aging. 2012 Dec;29(12):971-80. doi: 10.1007/s40266-012-0032-1. Drugs Aging. 2012. PMID: 23160960
-
Imaging the aging brain: study design and baseline findings of the SENIOR cohort.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2020 Jun 26;12(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s13195-020-00642-1. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32591008 Free PMC article.
-
Atorvastatin on Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients.Chonnam Med J. 2024 Jan;60(1):13-20. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2024.60.1.13. Epub 2024 Jan 25. Chonnam Med J. 2024. PMID: 38304133 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Castelli WP. Epidemiology of coronary heart disease: The Framingham study. Am J Med. 1984;76:4–12. - PubMed
-
- Stamler J, Wentworth D, Neaton JD. Is relationship between serum cholesterol and risk of premature death from coronary heart disease continuous and graded? Findings in 356,222 primary screenees of the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial (MRFIT) JAMA. 1986;256:2823–8. - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S, Reddy S, Ounpuu S, Anand S. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases: Part I: General considerations, the epidemiologic transition, risk factors, and impact of urbanization. Circulation. 2001;104:2746–53. - PubMed
-
- Influence of pravastatin and plasma lipids on clinical events in the West of Scotland. Coronary Prevention Study (WOSCOPS) Circulation. 1998;97:1440–5. - PubMed
-
- Heart Protection Study Collaborative Group. MRC/BHF Heart Protection Study of cholesterol lowering with simvastatin in 20,536 high-risk individuals: A randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;360:7–22. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
