Liver stem cells and tgf-Beta in hepatic carcinogenesis
- PMID: 19343145
- PMCID: PMC2661545
Liver stem cells and tgf-Beta in hepatic carcinogenesis
Abstract
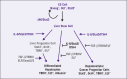
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the fifth most common malignancy worldwide. Recent trends indicate a rising incidence in the United States, with a 5-year survival rate of less than 5%. New therapeutics targeting advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma, such as sorafenib, have marginally improved the median overall survival by 3 months. There is an urgent need for new targeted agents that are associated with minimal local and systemic toxicities. Up to 40% of hepatocellular carcinomas are clonal, potentially arising from stem cells and increased activation of multiple pathways including IL-6/STAT3, WNT, CDK4, and hedgehog, as well as loss of response to the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) signaling pathway. Our hypothesis has been that these "cancer stem cells" or cancer sustaining cells may prove to be strong genetic and therapeutic targets. Modulating stem cell renewal factors such as STAT3, NANOG, and OCT4 may reduce hepatocellular carcinoma formation. These points are discussed in detail in this review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cancer stem cells and hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Biol Ther. 2009 Sep;8(18):1691-8. doi: 10.4161/cbt.8.18.9843. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19901516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coexpression of gene Oct4 and Nanog initiates stem cell characteristics in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of Stat3/Snail signaling.J Hematol Oncol. 2015 Mar 11;8:23. doi: 10.1186/s13045-015-0119-3. J Hematol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25879771 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Jak/Stat pathway as a therapeutic strategy against SP/CD44+ tumorigenic cells in Akt/β-catenin-driven hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hepatol. 2020 Jan;72(1):104-118. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.08.035. Epub 2019 Sep 18. J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31541681
-
Expression of Oct4 in HCC and modulation to wnt/β-catenin and TGF-β signal pathways.Mol Cell Biochem. 2010 Oct;343(1-2):155-62. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0509-3. Epub 2010 Jun 15. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20549546
-
Downregulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 by sorafenib: a novel mechanism for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Nov 7;20(41):15269-74. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15269. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25386075 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative study of the effects of PEGylated interferon-α2a versus 5-fluorouracil on cancer stem cells in a rat model of hepatocellular carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 Feb;37(2):1617-25. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3920-2. Epub 2015 Aug 26. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26304505
-
Investigating the functionality of an OCT4-short response element in human induced pluripotent stem cells.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2016 Jul 20;3:16050. doi: 10.1038/mtm.2016.50. eCollection 2016. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2016. PMID: 27500178 Free PMC article.
-
Links between cancer stem cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Onco Targets Ther. 2015 Oct 16;8:2973-80. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S91863. eCollection 2015. Onco Targets Ther. 2015. PMID: 26527883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Indirect Mechanisms of Transcription Factor-Mediated Gene Regulation during Cell Fate Changes.Adv Genet (Hoboken). 2022 Nov 9;3(4):2200015. doi: 10.1002/ggn2.202200015. eCollection 2022 Dec. Adv Genet (Hoboken). 2022. PMID: 36911290 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of cancer stem cells in liver cancer: current concepts and clinical implications.J Hepatol. 2010 Sep;53(3):568-77. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.05.003. Epub 2010 May 31. J Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 20646772 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Bray F, Pisani P, et al. GLOBOCAN 2002: Cancer Incidence, Mortality and Prevalence Worldwide. IARC Cancer Base No. 5. version 2.0. IARC Press; Lyon: 2004.
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, et al. Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer. 2001;94(2):153–156. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma: recent trends in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2004;127(5 suppl 1):S27–S34. - PubMed
-
- Roberts A, Mishra L. Role of TGF-beta in stem cells and cancer. Oncogene. 2005;24(37):5667. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
