Maximal extraction of biological information from genetic interaction data
- PMID: 19343223
- PMCID: PMC2659753
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000347
Maximal extraction of biological information from genetic interaction data
Abstract
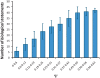
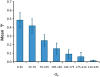
Extraction of all the biological information inherent in large-scale genetic interaction datasets remains a significant challenge for systems biology. The core problem is essentially that of classification of the relationships among phenotypes of mutant strains into biologically informative "rules" of gene interaction. Geneticists have determined such classifications based on insights from biological examples, but it is not clear that there is a systematic, unsupervised way to extract this information. In this paper we describe such a method that depends on maximizing a previously described context-dependent information measure to obtain maximally informative biological networks. We have successfully validated this method on two examples from yeast by demonstrating that more biological information is obtained when analysis is guided by this information measure. The context-dependent information measure is a function only of phenotype data and a set of interaction rules, involving no prior biological knowledge. Analysis of the resulting networks reveals that the most biologically informative networks are those with the greatest context-dependent information scores. We propose that these high-complexity networks reveal genetic architecture at a modular level, in contrast to classical genetic interaction rules that order genes in pathways. We suggest that our analysis represents a powerful, data-driven, and general approach to genetic interaction analysis, with particular potential in the study of mammalian systems in which interactions are complex and gene annotation data are sparse.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

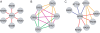

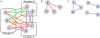

References
-
- Ideker T, Galitski T, Hood L. A new approach to decoding life: systems biology. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2001;2:343–372. - PubMed
-
- Tong AH, Lesage G, Bader GD, Ding H, Xu H, et al. Global mapping of the yeast genetic interaction network. Science. 2004;303:808–813. - PubMed
-
- Schuldiner M, Collins SR, Thompson NJ, Denic V, Bhamidipati A, et al. Exploration of the function and organization of the yeast early secretory pathway through an epistatic miniarray profile. Cell. 2005;123:507–519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

