Unique patterns of molecular profiling between human prostate cancer LNCaP and PC-3 cells
- PMID: 19343732
- PMCID: PMC2755240
- DOI: 10.1002/pros.20960
Unique patterns of molecular profiling between human prostate cancer LNCaP and PC-3 cells
Abstract
Background: Human prostate cancer LNCaP and PC-3 cell lines have been extensively used to study prostate cancer progression and to develop therapeutic agents. Although LNCaP and PC-3 cells are generally assumed to represent early and late stages of prostate cancer, respectively, there is limited information regarding gene expression patterns between these two cell lines and its relationship to prostate cancer.
Methods: Comprehensive gene expression analysis was performed. Total RNA was isolated from cultured cells and hybridized to Illumina human BeadChips representing 24,526 transcripts. Bioinformatics analysis was applied to identify cell line specific genes as well as biological mechanisms, pathways, and functions related to the genes.
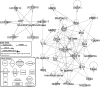
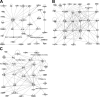
Results: A total of 2,198 genes were differentially expressed between LNCaP and PC-3 cells. Using a robust statistical analysis and high significance criteria, 115 and 188 genes were identified to be unique to LNCaP and PC-3 cells, respectively. LNCaP cells maintained various metabolic pathways including a gene cluster that encodes UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Several transcription factors including Tal alpha/beta, GATA-1, and c-Myc/Max may be responsible for regulating LNCaP cell specific genes. By contrast, PC-3 cells were characterized by their unique expression of cytoskeleton-related genes and other genes including VEGFC, IL8, and TGF beta 2.
Conclusions: This study showed that LNCaP and PC-3 cells represent two distinct prostate cancer cell lineages. LNCaP cells retain many prostate cell specific properties, whereas PC-3 cells have acquired a more aggressive phenotype. Future studies for prostate cancer research need to consider similarities and differences between these two cells and their relationship to prostate cancer.
(c) 2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
References
-
- Horoszewicz JS, Leong SS, Chu TM, Wajsman ZL, Friedman M, Papsidero L, Kim U, Chai LS, Kakati S, Arya SK, Sandberg AA. The LNCaP cell line--a new model for studies on human prostatic carcinoma. Progress in clinical and biological research. 1980;37:115–132. - PubMed
-
- Horoszewicz JS, Leong SS, Kawinski E, Karr JP, Rosenthal H, Chu TM, Mirand EA, Murphy GP. LNCaP model of human prostatic carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1983;43:1809–1818. - PubMed
-
- Veldscholte J, Voorhorst-Ogink MM, Bolt-de Vries J, van Rooij HC, Trapman J, Mulder E. Unusual specificity of the androgen receptor in the human prostate tumor cell line LNCaP: high affinity for progestagenic and estrogenic steroids. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 1990;1052:187–194. - PubMed
-
- Veldscholte J, Ris-Stalpers C, Kuiper GG, Jenster G, Berrevoets C, Claassen E, van Rooij HC, Trapman J, Brinkmann AO, Mulder E. A mutation in the ligand binding domain of the androgen receptor of human LNCaP cells affects steroid binding characteristics and response to anti-androgens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990;173:534–540. - PubMed
-
- Veldscholte J, Berrevoets CA, Ris-Stalpers C, Kuiper GGJM, Jenster G, Trapman J, Brinkmann AO, Mulder E. The androgen receptor in LNCaP cells contains a mutation in the ligand binding domain which affects steroid binding characteristics and response to antiandrogens. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1992;41:665–669. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous