Near-infrared imaging of injured tissue in living subjects using IR-820
- PMID: 19344575
- PMCID: PMC2790532
Near-infrared imaging of injured tissue in living subjects using IR-820
Abstract
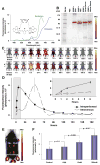
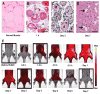
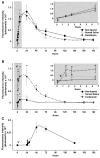
The unprecedented increase in preclinical studies necessitates high-throughput, inexpensive, and straightforward methods for evaluating diseased tissues. Near-infrared imaging of live subjects is a versatile, cost-effective technology that can be effectively used in a variety of pathologic conditions. We have characterized an inexpensive optoelectronic chemical, IR-820, as an infrared blood pool contrast agent to detect and quantify diseased tissue in live animals. IR-820 has maximal excitation and emission wavelengths of 710 and 820 nm, respectively. IR-820 emission is significantly improved in vivo on serum binding to albumin, and elimination occurs predominantly via the gastrointestinal tract. We demonstrate the utility of this contrast agent for serially imaging of traumatized tissue (muscle), tissue following reperfusion (eg, stroke), and tumors. IR-820 can also be employed to map regional lymph nodes. This novel contrast agent is anticipated to be a useful and an inexpensive tool for screening a wide variety of preclinical models of human diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Use of IR-820 as a preclinical/clinical contrast agent is under intellectual property evaluation by UTHSCSA.
Figures

References
-
- Sevick-Muraca EM, Houston JP, Gurfinkel M. Fluorescence-enhanced, near infrared diagnostic imaging with contrast agents. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2002;6:642–50. - PubMed
-
- Nomoto H, Shiraga F, Yamaji H, et al. Evaluation of radial optic neurotomy for central retinal vein occlusion by indocyanine green videoangiography and image analysis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004;138:612–9. - PubMed
-
- Nahrendorf M, Sosnovik DE, Waterman P, et al. Dual channel optical tomographic imaging of leukocyte recruitment and protease activity in the healing myocardial infarct. Circ Res. 2007;100:1218–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
