Acetylation targets mutant huntingtin to autophagosomes for degradation
- PMID: 19345187
- PMCID: PMC2940108
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.018
Acetylation targets mutant huntingtin to autophagosomes for degradation
Abstract
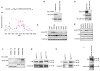
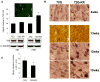
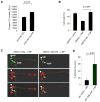
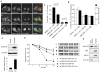
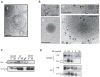
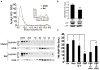
Huntington's disease (HD) is an incurable neurodegenerative disease caused by neuronal accumulation of the mutant protein huntingtin. Improving clearance of the mutant protein is expected to prevent cellular dysfunction and neurodegeneration in HD. We report here that such clearance can be achieved by posttranslational modification of the mutant Huntingtin (Htt) by acetylation at lysine residue 444 (K444). Increased acetylation at K444 facilitates trafficking of mutant Htt into autophagosomes, significantly improves clearance of the mutant protein by macroautophagy, and reverses the toxic effects of mutant huntingtin in primary striatal and cortical neurons and in a transgenic C. elegans model of HD. In contrast, mutant Htt that is rendered resistant to acetylation dramatically accumulates and leads to neurodegeneration in cultured neurons and in mouse brain. These studies identify acetylation as a mechanism for removing accumulated protein in HD, and more broadly for actively targeting proteins for degradation by autophagy.
Figures

References
-
- Arrasate M, Mitra S, Schweitzer ES, Segal MR, Finkbeiner S. Inclusion body formation reduces levels of mutant huntingtin and the risk of neuronal death. Nature. 2004;431:805–810. - PubMed
-
- Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T. The CBP co-activator is a histone acetyltransferase. Nature. 1996;384:641–643. - PubMed
-
- Cuervo AM. Autophagy: many paths to the same end. Mol Cell Biochem. 2004;263:55–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

