Separase is recruited to mitotic chromosomes to dissolve sister chromatid cohesion in a DNA-dependent manner
- PMID: 19345191
- PMCID: PMC2673135
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.040
Separase is recruited to mitotic chromosomes to dissolve sister chromatid cohesion in a DNA-dependent manner
Abstract
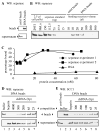
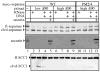
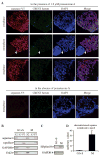
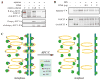
Sister chromatid separation is triggered by the separase-catalyzed cleavage of cohesin. This process is temporally controlled by cell-cycle-dependent factors, but its biochemical mechanism and spatial regulation remain poorly understood. We report that cohesin cleavage by human separase requires DNA in a sequence-nonspecific manner. Separase binds to DNA in vitro, but its proteolytic activity, measured by its autocleavage, is not stimulated by DNA. Instead, biochemical characterizations suggest that DNA mediates cohesin cleavage by bridging the interaction between separase and cohesin. In human cells, a fraction of separase localizes to the mitotic chromosome. The importance of the chromosomal DNA in cohesin cleavage is further demonstrated by the observation that the cleavage of the chromosome-associated cohesins is sensitive to nuclease treatment. Our observations explain why chromosome-associated cohesins are specifically cleaved by separase and the soluble cohesins are left intact in anaphase.
Figures

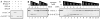

References
-
- Akhmedov AT, Gross B, Jessberger R. Mammalian SMC3 C-terminal and coiled-coil protein domains specifically bind palindromic DNA, do not block DNA ends, and prevent DNA bending. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:38216–38224. - PubMed
-
- Alexandru G, Uhlmann F, Mechtler K, Poupart MA, Nasmyth K. Phosphorylation of the cohesin subunit Scc1 by Polo/Cdc5 kinase regulates sister chromatid separation in yeast. Cell. 2001;105:459–472. - PubMed
-
- Fan HY, Sun QY, Zou H. Regulation of Separase in Meiosis: Separase is Activated at the Metaphase I-II Transition in Xenopus Oocytes during Meiosis. Cell Cycle. 2006;5:198–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

