Inactivation of Nxf2 causes defects in male meiosis and age-dependent depletion of spermatogonia
- PMID: 19345203
- PMCID: PMC2702087
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.03.022
Inactivation of Nxf2 causes defects in male meiosis and age-dependent depletion of spermatogonia
Abstract
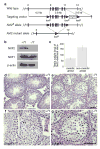
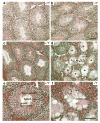
In eukaryotes, mRNA is actively transported from nucleus to cytoplasm by a family of nuclear RNA export factors (NXF). While yeast harbors only one such factor (Mex67p), higher eukaryotes encode multiple NXFs. In mouse, four Nxf genes have been identified: Nxf1, Nxf2, Nxf3, and Nxf7. To date, the function of mouse Nxf genes has not been studied by targeted gene deletion in vivo. Here we report the generation of Nxf2 null mutant mice by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Nxf2-deficient male mice exhibit fertility defects that differ between mouse strains. One third of Nxf2-deficient males on a mixed (C57BL/6x129) genetic background exhibit meiotic arrest and thus are sterile, whereas the remaining males are fertile. Disruption of Nxf2 in inbred (C57BL/6J) males impairs spermatogenesis, resulting in male subfertility, but causes no meiotic arrest. Testis weight and sperm output in C57BL/6J Nxf2(-/Y) mice are sharply reduced. Mutant epididymal sperm exhibit diminished motility. Importantly, proliferation of spermatogonia in Nxf2(-/Y) mice is significantly decreased. As a result, inactivation of Nxf2 causes depletion of germ cells in a substantial fraction of seminiferous tubules in aged mice. These studies demonstrate that Nxf2 plays a dual function in spermatogenesis: regulation of meiosis and maintenance of spermatogonial stem cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nxf3 is expressed in Sertoli cells, but is dispensable for spermatogenesis.Mol Reprod Dev. 2011 Apr;78(4):241-9. doi: 10.1002/mrd.21291. Epub 2011 Feb 9. Mol Reprod Dev. 2011. PMID: 21308854 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular cloning and functional characterization of mouse Nxf family gene products.Genomics. 2005 May;85(5):641-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2005.01.003. Genomics. 2005. PMID: 15820316
-
NXF2 is involved in cytoplasmic mRNA dynamics through interactions with motor proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(8):2513-21. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm125. Epub 2007 Apr 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17403691 Free PMC article.
-
The role of spermatogonially expressed germ cell-specific genes in mammalian meiosis.Chromosome Res. 2007;15(5):623-32. doi: 10.1007/s10577-007-1141-2. Chromosome Res. 2007. PMID: 17674150 Review.
-
Regulation of male fertility by X-linked genes.J Androl. 2010 Jan-Feb;31(1):79-85. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.109.008193. Epub 2009 Oct 29. J Androl. 2010. PMID: 19875494 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Embryonic lethality and defective male germ cell development in mice lacking UTF1.Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 8;7(1):17259. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17482-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29222434 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of the validated monogenic causes of human male infertility: 2020 update and a discussion of emerging gene-disease relationships.Hum Reprod Update. 2021 Dec 21;28(1):15-29. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmab030. Hum Reprod Update. 2021. PMID: 34498060 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory failure, cleft palate and epilepsy in the mouse model of human Xq22.1 deletion syndrome.Hum Mol Genet. 2014 Jul 15;23(14):3823-9. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu095. Epub 2014 Feb 25. Hum Mol Genet. 2014. PMID: 24569167 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of a proteome profile and identification of molecular markers for mouse spermatogonial stem cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2015 Mar;19(3):521-34. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12407. Epub 2014 Oct 29. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25352495 Free PMC article.
-
Ectopic Expression of Testis Germ Cell Proteins in Cancer and Its Potential Role in Genomic Instability.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 6;17(6):890. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060890. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27275820 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baker SM, Plug AW, Prolla TA, Bronner CE, Harris AC, Yao X, Christie DM, Monell C, Arnheim N, Bradley A, Ashley T, Liskay RM. Involvement of Mouse Mlh1 in DNA Mismatch Repair and Meiotic Crossing Over. Nat Genet. 1996;13:336–342. - PubMed
-
- Bakker CE, Verheij CE, Willemsen R, van der Helm R, Oerlemans F, Vermeij M, Bygrave A, Hoogeveen AT, Oostra BA, Reyniers E, De Boulle K, D'Hooge R, Cras P, van Velzen D, Nagels G, Martin J, De Deyn P, Darby JK, Willems PJ. Fmr1 Knockout Mice: A Model to Study Fragile X Mental Retardation the Dutch-Belgian Fragile X Consortium. Cell. 1994;78:23–33. - PubMed
-
- Buaas FW, Kirsh AL, Sharma M, McLean DJ, Morris JL, Griswold MD, de Rooij DG, Braun RE. Plzf is Required in Adult Male Germ Cells for Stem Cell Self-Renewal. Nat Genet. 2004;36:647–652. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

