Microtubule disassembly breaks down the barrier integrity of corneal endothelium
- PMID: 19345211
- PMCID: PMC2745835
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2009.03.019
Microtubule disassembly breaks down the barrier integrity of corneal endothelium
Abstract
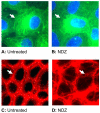
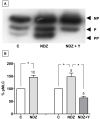
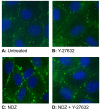
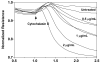
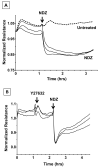
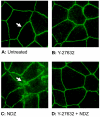
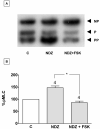
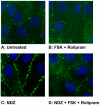
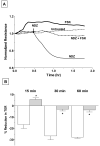
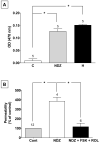
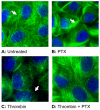
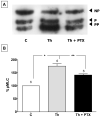
Increased contractility of the peri-junctional actomyosin ring (PAMR) breaks down the barrier integrity of corneal endothelium. This study has examined the effects of microtubule disassembly on Myosin Light Chain (MLC) phosphorylation, a biochemical marker of actomyosin contraction, and barrier integrity in monolayers of cultured bovine corneal endothelial cells (BCEC). Exposure to nocodazole, which readily induced microtubule disassembly, led to disruption of the characteristically dense assembly of cortical actin cytoskeleton at the apical junctional complex (i.e., PAMR) and dispersion of ZO-1 from its normal locus. Nocodazole also led to an increase in phosphorylation of MLC. Concomitant with these changes, nocodazole caused an increase in permeability to HRP and FITC dextran (10 kDa) and a decrease in trans-endothelial electrical resistance (TER). Y-27632 (a Rho kinase inhibitor) and forskolin (known to inhibit activation of RhoA through direct elevation of cAMP) opposed the nocodazole-induced MLC phosphorylation, decrease in TER, and dispersion of ZO-1. Thrombin, which breaks down the barrier integrity of BCEC monolayers, also induced microtubule disassembly and MLC phosphorylation. Pre-treatment with paclitaxel to stabilize microtubules opposed the thrombin effects. These results suggest that microtubule disassembly breaks down the barrier integrity of BCEC through activation of RhoA and subsequent disruption of the PAMR. The thrombin effect also highlights that signaling downstream of GPCRs can also influence the organization of microtubules.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lovastatin inhibits the thrombin-induced loss of barrier integrity in bovine corneal endothelium.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Feb;26(1):1-10. doi: 10.1089/jop.2009.0025. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20148651 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombin-induced phosphorylation of the regulatory light chain of myosin II in cultured bovine corneal endothelial cells.Exp Eye Res. 2004 Oct;79(4):477-86. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2004.06.018. Exp Eye Res. 2004. PMID: 15381032
-
Elevated cAMP opposes (TNF-alpha)-induced loss in the barrier integrity of corneal endothelium.Mol Vis. 2010 Sep 2;16:1781-90. Mol Vis. 2010. PMID: 20824160 Free PMC article.
-
Cell signaling in regulation of the barrier integrity of the corneal endothelium.Exp Eye Res. 2012 Feb;95(1):8-15. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2011.09.009. Epub 2011 Sep 24. Exp Eye Res. 2012. PMID: 21963716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of thrombin-induced endothelial cell permeability.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2002 Jan;67(1):75-84. doi: 10.1023/a:1013904231324. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2002. PMID: 11841342 Review.
Cited by
-
The Endothelial Centrosome: Specific Features and Functional Significance for Endothelial Cell Activity and Barrier Maintenance.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 20;24(20):15392. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015392. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Barrier dysfunction of the corneal endothelium in response to TNF-alpha: role of p38 MAP kinase.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Mar;51(3):1575-82. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-4343. Epub 2009 Sep 24. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 19797215 Free PMC article.
-
Role of cAMP-dependent protein kinase A activity in low-dose endothelial monocyte-activating polypeptide-II-induced opening of blood-tumor barrier.J Mol Neurosci. 2015 May;56(1):60-9. doi: 10.1007/s12031-014-0467-4. Epub 2014 Nov 22. J Mol Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25416651
-
Formation and disassembly of adherens and tight junctions in the corneal endothelium: regulation by actomyosin contraction.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Apr;51(4):2139-48. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-4421. Epub 2009 Dec 17. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 20019371 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Dose Endothelial Monocyte-Activating Polypeptide-II Induces Blood-Tumor Barrier Opening Via the cAMP/PKA/Rac1 Pathway.J Mol Neurosci. 2016 Feb;58(2):153-61. doi: 10.1007/s12031-015-0649-8. Epub 2015 Sep 10. J Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26358039
References
-
- Ayala A, Warejcka DJ, et al. Corneal activation of prothrombin to form thrombin, independent of vascular injury. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48(1):134–43. - PubMed
-
- Banan A, Farhadi A, et al. The delta-isoform of protein kinase C causes inducible nitric-oxide synthase and nitric oxide up-regulation: key mechanism for oxidant-induced carbonylation, nitration, and disassembly of the microtubule cytoskeleton and hyperpermeability of barrier of intestinal epithelia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;305(2):482–94. - PubMed
-
- Bereiter-Hahn J, Voth M, et al. Structural implications of mitochondrial dynamics. Biotechnol J. 2008;3(6):765–80. - PubMed
-
- Birukova AA, Adyshev D, et al. GEF-H1 is involved in agonist-induced human pulmonary endothelial barrier dysfunction. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006;290(3):L540–8. - PubMed
-
- Birukova AA, Birukov KG, et al. Involvement of microtubules and Rho pathway in TGF-beta1-induced lung vascular barrier dysfunction. J Cell Physiol. 2005;204(3):934–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

