Geometric and electronic structure differences between the type 3 copper sites of the multicopper oxidases and hemocyanin/tyrosinase
- PMID: 19346471
- PMCID: PMC2672473
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0902127106
Geometric and electronic structure differences between the type 3 copper sites of the multicopper oxidases and hemocyanin/tyrosinase
Abstract
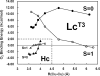
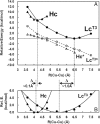
The coupled binuclear "type 3" Cu sites are found in hemocyanin (Hc), tyrosinase (Tyr), and the multicopper oxidases (MCOs), such as laccase (Lc), and play vital roles in O(2) respiration. Although all type 3 Cu sites share the same ground state features, those of Hc/Tyr have very different ligand-binding properties relative to those of the MCOs. In particular, the type 3 Cu site in the MCOs (Lc(T3)) is a part of the trinuclear Cu cluster, and if the third (i.e., type 2) Cu is removed, the Lc(T3) site does not react with O(2). Density functional theory calculations indicate that O(2) binding in Hc is approximately 9 kcal mol(-1) more favorable than for Lc(T3). The difference is mostly found in the total energy difference of the deoxy states (approximately 7 kcal mol(-1)), where the stabilization of deoxy Lc(T3) derives from its long equilibrium Cu-Cu distance of approximately 5.5-6.5 A, relative to approximately 4.2 A in deoxy Hc/Tyr. The O(2) binding in Hc is driven by the electrostatic destabilization of the deoxy Hc site, in which the two Cu(I) centers are kept close together by the protein for facile 2-electron reduction of O(2). Alternatively, the lack of O(2) reactivity in Lc(T3) reflects the flexibility of the active site, capable of minimizing the electrostatic repulsion of the 2 Cu(I)s. Thus, the O(2) reactivity of the MCOs is intrinsic to the trinuclear Cu cluster, leading to different O(2) intermediates as required by its function of irreversible reduction of O(2) to H(2)O.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Malkin R, Malmström BG. State and function of copper in biological systems. Adv Enzymol. 1970;33:177–244. - PubMed
-
- Solomon EI, Chen P, Metz M, Lee SK, Palmer AE. Oxygen binding, activation, and reduction to water by copper proteins. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2001;40:4570–4590. - PubMed
-
- Solomon EI, Sundaram UM, Machonkin TE. Multicopper oxidases and oxygenases. Chem Rev. 1996;96:2563–2605. - PubMed
-
- Gaykema WPJ, et al. 3.2 Å structure of the copper-containing, oxygen-carrying protein Panulirus interruptus haemocyanin. Nature. 1984;309:23–29.
-
- Volbeda A, Hol WGJ. Crystal structure of hexameric haemocyanin from Panulirus interruptus refined at 3.2 Å resolution. J Mol Biol. 1989;209:249–279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

