Molecular, serological and biological variation among chickpea chlorotic stunt virus isolates from five countries of North Africa and West Asia
- PMID: 19347243
- PMCID: PMC3085786
- DOI: 10.1007/s00705-009-0374-0
Molecular, serological and biological variation among chickpea chlorotic stunt virus isolates from five countries of North Africa and West Asia
Abstract
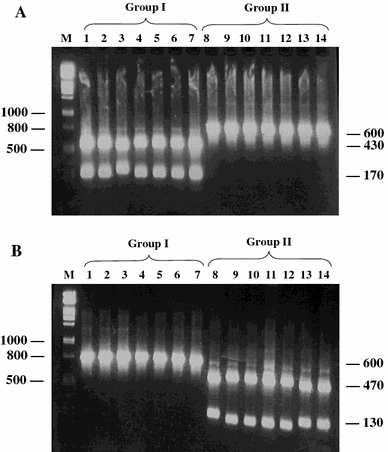
Chickpea chlorotic stunt virus (CpCSV), a proposed new member of the genus Polerovirus (family Luteoviridae), has been reported only from Ethiopia. In attempts to determine the geographical distribution and variability of CpCSV, a pair of degenerate primers derived from conserved domains of the luteovirus coat protein (CP) gene was used for RT-PCR analysis of various legume samples originating from five countries and containing unidentified luteoviruses. Sequencing of the amplicons provided evidence for the occurrence of CpCSV also in Egypt, Morocco, Sudan, and Syria. Phylogenetic analysis of the CP nucleotide sequences of 18 samples from the five countries revealed the existence of two geographic groups of CpCSV isolates differing in CP sequences by 8-10%. Group I included isolates from Ethiopia and Sudan, while group II comprised those from Egypt, Morocco and Syria. For distinguishing these two groups, a simple RFLP test using HindIII and/or PvuII for cleavage of CP-gene-derived PCR products was developed. In ELISA and immunoelectron microscopy, however, isolates from these two groups could not be distinguished with rabbit antisera raised against a group-I isolate from Ethiopia (CpCSV-Eth) and a group-II isolate from Syria (CpCSV-Sy). Since none of the ten monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) that had been produced earlier against CpCSV-Eth reacted with group-II isolates, further MAbs were produced. Of the seven MAbs raised against CpCSV-Sy, two reacted only with CpCSV-Sy and two others with both CpCSV-Sy and -Eth. This indicated that there are group I- and II-specific and common (species-specific) epitopes on the CpCSV CP and that the corresponding MAbs are suitable for specific detection and discrimination of CpCSV isolates. Moreover, CpCSV-Sy (group II) caused more severe stunting and yellowing in faba bean than CpCSV-Eth (group I). In conclusion, our data indicate the existence of a geographically associated variation in the molecular, serological and presumably biological properties of CpCSV.
Figures



References
-
- Abraham AD, Makkouk KM, Gorfu D, Lencho AG, Ali K, Tadesse N, Yusuf A, Lencho A. Survey of faba bean (Vicia faba L.) virus diseases in Ethiopia. Phytopathol Mediterr. 2000;39:277–282.
-
- Abraham AD, Varrelmann M, Vetten HJ. Molecular evidence for the occurrence of two new luteoviruses in cool season food legumes in Northeast Africa. Afr J Biotechnol. 2008;7:414–420.
-
- Adam G, Lesemann D-E, Vetten HJ. Monoclonal antibodies against tomato spotted wilt virus: characterization and application. Ann Appl Biol. 1991;118:87–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7348.1991.tb06088.x. - DOI
-
- Bos L, Hampton RO, Makkouk KM. Viruses and virus diseases of pea, lentil, faba bean and chickpea. In: Summerfield RJ, editor. World crops; cool season food legumes. Dordrecht: Kluwer; 1988. pp. 591–615.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

