High-content screening: flow cytometry analysis
- PMID: 19347622
- PMCID: PMC4476789
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-60327-545-3_11
High-content screening: flow cytometry analysis
Abstract
The HyperCyt high-throughput (HT) flow cytometry sampling platform uses a peristaltic pump, in combination with an autosampler, and a novel approach to data collection, to circumvent time-delay bottlenecks of conventional flow cytometry. This approach also dramatically reduces the amount of sample aspirated for each analysis, typically requiring ~2 microL per sample while making quantitative fluorescence measurements of 40 or more samples per minute with thousands to tens of thousands of cells in each sample. Here, we describe a simple robust screening assay that exploits the high-content measurement capabilities of the flow cytometer to simicroltaneously probe the binding of test compounds to two different receptors in a common assay volume, a duplex assay format. The ability of the flow cytometer to distinguish cell-bound from free fluorophore is also exploited to eliminate wash steps during assay setup. HT flow cytometry with this assay has allowed efficient screening of tens of thousands of small molecules from the NIH Small-Molecule Repository to identify selective ligands for two related G-protein-coupled receptors, the formylpeptide receptor and formylpeptide receptor-like 1.
Figures

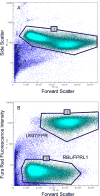
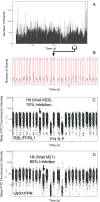
References
-
- Kuckuck FW, Edwards BS, Sklar LA. Cytometry. 2001;44:83–90. - PubMed
-
- Ramirez S, Aiken CT, Andrzejewski B, Sklar LA, Edwards BS. Cytometry. 2003;53A:55–65. - PubMed
-
- Young SM, Bologa C, Prossnitz E, Oprea TI, Sklar LA, Edwards BS. J Biomol Screen. 2004;10:374–382. - PubMed
-
- Edwards BS, Bologa C, Young SM, Balakin KV, Prossnitz E, Savchuck NP, Sklar LA, Oprea TI. Mol Pharmacol. 2005;68:1301–1310. - PubMed
-
- Edwards BS, Young SM, Oprea TI, Bologa C, Prossnitz E, Sklar LA. Nat Protocols. 2006;1:59–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

