Habituation as a determinant of human food intake
- PMID: 19348547
- PMCID: PMC2703585
- DOI: 10.1037/a0015074
Habituation as a determinant of human food intake
Abstract
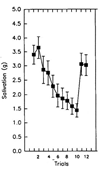
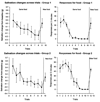
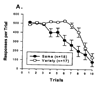
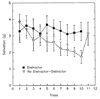
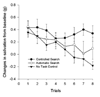
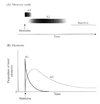
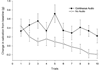
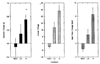
Research has shown that animals and humans habituate on a variety of behavioral and physiological responses to repeated presentations of food cues, and habituation is related to amount of food consumed and cessation of eating. The purpose of this article is to provide an overview of experimental paradigms used to study habituation, integrate a theoretical approach to habituation to food based on memory and associative conditioning models, and review research on factors that influence habituation. Individual differences in habituation as they relate to obesity and eating disorders are reviewed, along with research on how individual differences in memory can influence habituation. Other associative conditioning approaches to ingestive behavior are reviewed, as well as how habituation provides novel approaches to preventing or treating obesity. Finally, new directions for habituation research are presented. Habituation provides a novel theoretical framework from which to understand factors that regulate ingestive behavior.
(c) 2009 APA, all rights reserved
Figures

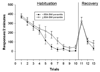
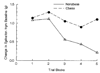
Similar articles
-
Food reinforcement and habituation to food are processes related to initiation and cessation of eating.Physiol Behav. 2021 Oct 1;239:113512. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2021.113512. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Physiol Behav. 2021. PMID: 34217735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term habituation to food in obese and nonobese women.Am J Clin Nutr. 2011 Aug;94(2):371-6. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.110.009035. Epub 2011 May 18. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21593492 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Habituation and within-session changes in motivated responding for food in children.Appetite. 2008 Mar-May;50(2-3):390-6. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2007.09.005. Epub 2007 Sep 21. Appetite. 2008. PMID: 17961817 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of allocation of attention on habituation to olfactory and visual food stimuli in children.Physiol Behav. 2005 Feb 15;84(2):313-9. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2004.12.009. Epub 2005 Jan 16. Physiol Behav. 2005. PMID: 15708783
-
External cues challenging the internal appetite control system-Overview and practical implications.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017 Sep 2;57(13):2825-2834. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2015.1073140. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017. PMID: 26463499 Review.
Cited by
-
Food characteristics, long-term habituation and energy intake. Laboratory and field studies.Appetite. 2013 Jan;60(1):40-50. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2012.08.030. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Appetite. 2013. PMID: 23085682 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Within- and between-session variety effects in a food-seeking habituation paradigm.Appetite. 2013 Jul;66:10-9. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2013.01.025. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Appetite. 2013. PMID: 23434973 Free PMC article.
-
Variety influences habituation of motivated behavior for food and energy intake in children.Am J Clin Nutr. 2009 Mar;89(3):746-54. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2008.26911. Epub 2009 Jan 28. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009. PMID: 19176724 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
An exploration of salivation patterns in normal weight and obese children.Appetite. 2012 Apr;58(2):539-42. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2011.11.027. Epub 2011 Dec 3. Appetite. 2012. PMID: 22172456 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of repetitive imagination of alcohol consumption on craving in alcohol-dependent patients: A pilot study.Addict Behav Rep. 2016 Aug 7;4:51-57. doi: 10.1016/j.abrep.2016.08.001. eCollection 2016 Dec. Addict Behav Rep. 2016. PMID: 29511724 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson MC, Ochsner KN, Kuhl B, Cooper J, Robertson E, Gabrieli SW, et al. Neural systems underlying the suppression of unwanted memories. Science. 2004;303:232–235. - PubMed
-
- Baker TB, Tiffany ST. Morphine tolerance as habituation. Psychological Review. 1985;92:78–108. - PubMed
-
- Bartoshuk LM. Taste, smell and pleasure. In: Bolles RC, editor. The hedonics of taste. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc; 1991. pp. 15–28.
-
- Batterham RL, Cohen MA, Ellis SM, Le Roux CW, Withers DJ, Frost GS, et al. Inhibition of food intake in obese subjects by peptide YY3–36. New England Journal of Medicine. 2003;349:941–948. - PubMed
-
- Batterham RL, Cowley MA, Small CJ, Herzog H, Cohen MA, Dakin CL, et al. Gut hormone PYY(3–36) physiologically inhibits food intake. Nature. 2002;418:650–654. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

