Stimulation with Peptidoglycan induces interleukin 6 and TLR2 expression and a concomitant downregulation of expression of adiponectin receptors 1 and 2 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- PMID: 19348674
- PMCID: PMC2670298
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-9255-6-8
Stimulation with Peptidoglycan induces interleukin 6 and TLR2 expression and a concomitant downregulation of expression of adiponectin receptors 1 and 2 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
Abstract
Background: Inflammation is a major component of obesity and diabetes, and toll-like receptors (TLRs) play critical roles in the regulation of inflammation and response to pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and fatty acids in. Although immune cells such as macrophages are primarily responsible for recognition and clearance of pathogens, adipocytes are also closely involved in the regulation of innate immunity and inflammation. Whereas it has been demonstrated that adipocytes respond to TLR4 stimulation with lipopolysacccharide, very little is known about their response to the TLR2 agonist, peptidoglycan.
Methods: We investigated the response to peptidoglycan from Staphylococcus aureus in differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Real-time PCR analysis was used to quantify the expression of interleukin 6 (IL6), adiponectin receptors (adipoR1 and adipoR2), toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and 4 (TLR2 4). Media level of IL6 was determined with ELISA.
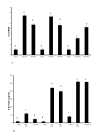
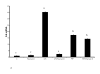
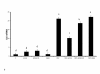
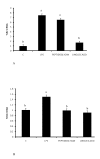
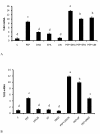
Results: Adipocyte stimulation peptidoglycan induces IL6 expression (P < 0.01). Both siRNA mediated suppression of TLR2 and immunoneutralization of TLR2 with a TLR2 specific antibody inhibited response to peptidoglycan (P < 0.05). We also examined the regulation of TLR2 and TLR4 mRNA in peptidoglycan treated cells. Both peptidoglycan and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) robustly induce TLR2 mRNA expression, whereas TLR4 mRNA is weakly induced by LPS only (P < 0.05). Additionally, peptidoglycan downregulates the mRNA expression of adiponectin receptors, adipoR1 and adipoR2 (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Obesity and type 2 diabetes are associated with increased expression of TLR2, this receptor could play a significant but previously unrecognized role in the establishment of chronic inflammation in adipose tissue in obesity.
Figures

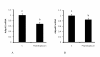
References
-
- Ajuwon KM, Jacobi SK, Kuske JL, Spurlock ME. Interleukin-6 and interleukin-15 are selectively regulated by lipopolysaccharide and interferon-gamma in primary pig adipocytes. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2004;286:R547–R553. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

