TRAIL, DR4 and DR5 are upregulated in kidneys from patients with lupus nephritis and exert proliferative and proinflammatory effects
- PMID: 19349211
- PMCID: PMC3734543
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2009.02.011
TRAIL, DR4 and DR5 are upregulated in kidneys from patients with lupus nephritis and exert proliferative and proinflammatory effects
Abstract
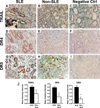
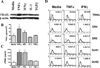
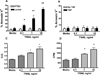
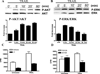
We have previously reported that TRAIL is upregulated on T cells from patients with lupus and that T cell associated TRAIL enhances autoimmune parameters in a murine model of lupus. Whether TRAIL/TRAIL-R interaction plays a role in organ involvement such as lupus nephritis has not yet been assessed. We demonstrate here that TRAIL, DR4 and DR5 are upregulated in proximal and distal tubules of patients with proliferative lupus nephritis. In vitro, expression of TRAIL, DR4 and DR5 on primary proximal tubular epithelial cells (PTEC) was induced by TNFalpha and IFNgamma. Functionally, TRAIL did not induce apoptosis but rather enhanced the proliferation of PTEC through activation of PI3 kinase/AKT and ERK1/2, increased IL-8 production and upregulated ICAM-1 expression. These data demonstrate that cytokine induced upregulation of TRAIL, DR4 and DR5 in tubules from patients with proliferative lupus nephritis may play a protective role by enhancing PTEC survival while also exerting a proinflammatory effect that may contribute to local inflammation and injury.
Figures
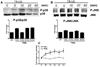
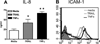
Similar articles
-
Expression of TRAIL and the death receptors DR4 and DR5 correlates with progression of degeneration in human intervertebral disks.Mod Pathol. 2009 Jul;22(7):895-905. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2009.39. Epub 2009 Mar 20. Mod Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19305384
-
Effects and expression of TRAIL and its apoptosis-promoting receptors in human pancreatic cancer.Cancer Lett. 2001 Feb 10;163(1):71-81. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(00)00660-1. Cancer Lett. 2001. PMID: 11163110
-
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) up-regulates death receptor 5 (DR5) mediated by NFkappaB activation in epithelial derived cell lines.Apoptosis. 2002 Oct;7(5):413-20. doi: 10.1023/a:1020031023947. Apoptosis. 2002. PMID: 12207174
-
Trail and kidney disease.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009 Jan 1;14(10):3740-9. doi: 10.2741/3485. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009. PMID: 19273307 Review.
-
Mediators of inflammation and their effect on resident renal cells: implications in lupus nephritis.Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:317682. doi: 10.1155/2013/317682. Epub 2013 Sep 22. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24171032 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TRAIL, OPG, and TWEAK in kidney disease: biomarkers or therapeutic targets?Clin Sci (Lond). 2019 May 16;133(10):1145-1166. doi: 10.1042/CS20181116. Print 2019 May 31. Clin Sci (Lond). 2019. PMID: 31097613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Reprogramming of Innate Immune Cells as a Possible Source of New Therapeutic Approaches in Autoimmunity.Cells. 2022 May 17;11(10):1663. doi: 10.3390/cells11101663. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35626700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and validation of key autophagy-related genes in lupus nephritis by bioinformatics and machine learning.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 27;20(1):e0318280. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0318280. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39869603 Free PMC article.
-
The Genetic Landscape of Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 2;9:916011. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.916011. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35721085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blocking TRAIL-DR5 signaling with soluble DR5 alleviates acute kidney injury in a severely burned mouse model.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 May 15;7(6):3460-8. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25031778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jeremias I, Herr I, Boehler T, Debatin KM. TRAIL/Apo-2-ligand-induced apoptosis in human T cells. Eur.J Immunol. 1998;28:143–152. - PubMed
-
- Morel J, Audo R, Hahne M, Combe B. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) induces rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblast proliferation through mitogen-activated protein kinases and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:15709–15718. - PubMed
-
- Li JH, Kirkiles-Smith NC, McNiff JM, Pober JS. TRAIL induces apoptosis and inflammatory gene expression in human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 2003;171:1526–1533. - PubMed
-
- Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS, Huang CP, Nicholl JK, Sutherland GR, Smith TD, Rauch C, Smith CA, et al. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 1995;3:673–682. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhary PM, Eby M, Jasmin A, Bookwalter A, Murray J, Hood L. Death receptor 5, a new member of the TNFR family, and DR4 induce FADD-dependent apoptosis and activate the NF-kappaB pathway. Immunity. 1997;7:821–830. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

