Phase III trial of irinotecan/cisplatin compared with etoposide/cisplatin in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: clinical and pharmacogenomic results from SWOG S0124
- PMID: 19349543
- PMCID: PMC2684855
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2008.20.1061
Phase III trial of irinotecan/cisplatin compared with etoposide/cisplatin in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: clinical and pharmacogenomic results from SWOG S0124
Abstract
Purpose: Irinotecan plus cisplatin (IP) improved survival over etoposide plus cisplatin (EP) in Japanese patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (E-SCLC). To confirm those results and discern the potential role of population-related pharmacogenomics (PG) in outcomes, we conducted a large randomized trial of identical design to the Japanese trial in North American patients with E-SCLC.
Patients and methods: Patients were randomly assigned to IP (irinotecan 60 mg/m(2) on days 1, 8, and 15; cisplatin 60 mg/m(2) day 1, every 4 weeks) or EP (etoposide 100 mg/m(2) on days 1 through 3; cisplatin 80 mg/m(2) day 1, every 3 weeks). Blood specimens for genomic DNA analysis were collected before random assignment in 169 patients.
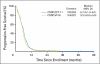
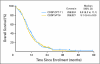
Results: Of 671 patients, 651 were eligible (324 and 327 patients in the IP and EP arms, respectively). Response rates with IP and EP were 60% and 57%, respectively (P = .56). Median progression-free survival for IP and EP was 5.8 and 5.2 months, respectively (P = .07). Median overall survival for IP and EP was 9.9 and 9.1 months, respectively (P = .71). Severe diarrhea was more common with IP (19% v 3%); severe neutropenia and thrombocytopenia were higher with EP versus IP (68% v 33% and 15% v 4%, respectively). PG analysis showed that ABCB1 (C3435T)T/T (membrane transport) was associated with IP-related diarrhea; UGT1A1 (G-3156A)A/A (drug metabolism) was associated with IP-related neutropenia.
Conclusion: This large North American trial failed to confirm the previously reported survival benefit observed with IP in Japanese patients. Both regimens produced comparable efficacy, with less hematologic and greater gastrointestinal toxicity with IP. These results emphasize the potential importance of PG in interpreting trials of cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Govindan R, Page N, Morgensztern N, et al. Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: Analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiologic, and End Results database. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4539–4544. - PubMed
-
- Clark R, Ihde DC. Small cell lung cancer: Treatment progress and prospects. Oncology (Williston Park) 1998;12:647–658. - PubMed
-
- Albain KS, Crowley JJ, LeBlanc M, et al. Determinants of improved outcome in small cell lung cancer: An analysis of the 2,580 patient Southwest Oncology Group database. J Clin Oncol. 1990;8:1563–1574. - PubMed
-
- Schiller JH, Adak S, Cella D, et al. Topotecan versus observation after cisplatin plus etoposide in extensive stage small cell lung cancer: E7593—A phase III trial of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:2114–2122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA22433/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA045807/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA63850/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76447/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046368/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA63848/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA027525/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA37981/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58348/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58416/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035176/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35128/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35261/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045560/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA12644/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035128/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA20319/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063850/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA013612/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035192/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA114771/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035279/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA021115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA013612/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58658/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA27525/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA68183/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA014028/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180846/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA046441/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063848/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35279/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA14028/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45377/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA074647/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA11083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76132/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA063844/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035261/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA16385/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045450/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45450/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46368/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA67663/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA038926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA067575/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046441/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045377/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35192/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233340/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA74647/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA020319/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA038926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA114771/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76448/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA042777/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA42777/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA011083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA52654/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA052654/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA067575/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA067663/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA21115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76429/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035176/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58723/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063844/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045807/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA045560/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

