Comprehensive quantification of ceramide species in human stratum corneum
- PMID: 19349641
- PMCID: PMC2724059
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.D800055-JLR200
Comprehensive quantification of ceramide species in human stratum corneum
Abstract
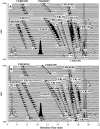
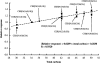
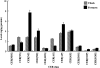
One of the key challenges in lipidomics is to quantify lipidomes of interest, as it is practically impossible to collect all authentic materials covering the targeted lipidomes. For diverse ceramides (CER) in human stratum corneum (SC) that play important physicochemical roles in the skin, we developed a novel method for quantification of the overall CER species by improving our previously reported profiling technique using normal-phase liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (NPLC-ESI-MS). The use of simultaneous selected ion monitoring measurement of as many as 182 kinds of molecular-related ions enables the highly sensitive detection of the overall CER species, as they can be analyzed in only one SC-stripped tape as small as 5 mm x 10 mm. To comprehensively quantify CERs, including those not available as authentic species, we designed a procedure to estimate their levels using relative responses of representative authentic species covering the species targeted, considering the systematic error based on intra-/inter-day analyses. The CER levels obtained by this method were comparable to those determined by conventional thin-layer chromatography (TLC), which guarantees the validity of this method. This method opens lipidomics approaches for CERs in the SC.
Figures

References
-
- Spener F., Lagarde M., Geloen A., Record M. 2003. What is lipidomics? Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 105: 481–482
-
- Mano N., Oda Y., Yamada K., Asakawa N., Katayama K. 1997. Simultaneous quantitative determination method for sphingolipid metabolites by liquid chromatography/ionspray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 244: 291–300 - PubMed
-
- Han X., Gross R. W. 2001. Quantitative analysis and molecular species fingerprinting of triacylglyceride molecular species directly from lipid extracts of biological samples by electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 295: 88–100 - PubMed
-
- Koivusalo M., Haimi P., Heikinheimo L., Kostiainen R., Somerharju P. 2001. Quantitative determination of phospholipid compositions by ESI-MS: effects of acyl chain length, unsaturation, and lipid concentration on instrument response. J. Lipid Res. 42: 663–672 - PubMed
-
- Han X., Gross R. W. 2003. Global analyses of cellular lipidomes directly from crude extracts of biological samples by ESI tandem mass spectrometry: a bridge to lipidomics. J. Lipid Res. 44: 1071–1079 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

