Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis induced in mice lacking decay-accelerating factor in T cells
- PMID: 19349693
- PMCID: PMC2673859
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI36000
Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis induced in mice lacking decay-accelerating factor in T cells
Abstract
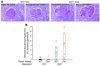
Heritable and acquired diseases of podocytes can result in focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). We modeled FSGS by passively transferring mouse podocyte-specific sheep Abs into BALB/c mice. BALB/c mice deficient in the key complement regulator, decay-accelerating factor (DAF), but not WT or CD59-deficient BALB/c mice developed histological and ultrastructural features of FSGS, marked albuminuria, periglomerular monocytic and T cell inflammation, and enhanced T cell reactivity to sheep IgG. All of these findings, which are characteristic of FSGS, were substantially reduced by depleting CD4+ T cells from Daf(-/-) mice. Furthermore, WT kidneys transplanted into Daf(-/-) recipients and kidneys of DAF-sufficient but T cell-deficient Balb/(cnu/nu) mice reconstituted with Daf(-/-) T cells developed FSGS. In contrast, DAF-deficient kidneys in WT hosts and Balb/(cnu/nu) mice reconstituted with DAF-sufficient T cells did not develop FSGS. Thus, we have described what we believe to be a novel mouse model of FSGS attributable to DAF-deficient T cell immune responses. These findings add to growing evidence that complement-derived signals shape T cell responses, since T cells that recognize sheep Abs bound to podocytes can lead to cellular injury and development of FSGS.
Figures




References
-
- Speth, C., Prodinger, W.M., Würzner, R., Stoibert, H., and Dierich, M.P. 1993. Complement. In Fundamental immunology. 6th edition. W.E. Paul, editor. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Baltimore, Maryland, USA. 1047–1078.
-
- Holers, V.M. 2001. Complement deficiencies. In Clinical immunology: principles and practice. 2nd edition. R. Rich, editor. Mosby. St. Louis, Missouri, USA. 36.1–36.10.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI063288/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI049344/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK056799/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK041873/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI049344/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI044970/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR049775/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK051096/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK055357/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI049344/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK056799/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK041873/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK066802/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK066802/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI063288/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AR049775/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK051096/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI044970/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

