The stiff elbow
- PMID: 19350328
- PMCID: PMC2787214
- DOI: 10.1007/s11552-009-9181-z
The stiff elbow
Abstract
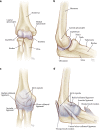
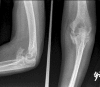
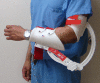
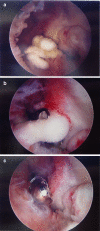
Elbow motion is essential for upper extremity function to position the hand in space. Unfortunately, the elbow joint is prone to stiffness following a multitude of traumatic and atraumatic etiologies. Elbow stiffness can be diagnosed with a complete history and physical exam, supplemented with appropriate imaging studies. The stiff elbow is challenging to treat, and thus, its prevention is of paramount importance. When this approach fails, non-operative followed by operative treatment modalities should be pursued. Upon initial presentation in those who have minimal contractures of 6-month duration or less, static and dynamic splinting, serial casting, continuous passive motion, occupational/physical therapy, and manipulation are non-operative treatment modalities that may be attempted. A stiff elbow that is refractory to non-operative management can be treated surgically, either arthroscopically or open, to eliminate soft tissue or bony blocks to motion. In the future, efforts to prevent and treat elbow stiffness may target the basic science mechanisms involved. Our purpose was to review the etiologies, classification, evaluation, prevention, operative, and non-operative treatment of the stiff elbow.
Figures





References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1097/00006534-197301000-00014', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-197301000-00014'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '4347108', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4347108/'}]}
- Apfelberg DB, Larson SJ. Dynamic anatomy of the ulnar nerve at the elbow. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1973;51(1):79–81. doi:10.1097/00006534-197301000-00014. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S1058-2746(98)90035-0', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s1058-2746(98)90035-0'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9752655', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9752655/'}]}
- Bain GI, Mehta JA, Heptinstall RJ. The dynamic elbow suspension splint. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1998;7(4):419–21. doi:10.1016/S1058-2746(98)90035-0. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1080/13693780500402229', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1080/13693780500402229'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16449076', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16449076/'}]}
- Basciani M, Intiso D. Botulinum toxin type-A and plaster cast treatment in children with upper brachial plexus palsy. Pediatr Rehabil. 2006;9(2):165–70. doi:10.1080/13693780500402229. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '2398084', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2398084/'}]}
- Bidner SM, Rubins IM, Desjardins JV, Zukor DJ, Goltzman D. Evidence for a humoral mechanism for enhanced osteogenesis after head injury. J Bone Jt Surg Am. 1990;72(8):1144–9. - PubMed
-
- Bonutti PM, Windau JE, Ables BA, Miller BG. Static progressive stretch to reestablish elbow range of motion. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;(303):128–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

