Visuo-attentional and sensorimotor alpha rhythms are related to visuo-motor performance in athletes
- PMID: 19350556
- PMCID: PMC6870716
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.20776
Visuo-attentional and sensorimotor alpha rhythms are related to visuo-motor performance in athletes
Abstract
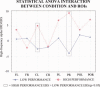
This study tested the two following hypotheses: (i) compared with non-athletes, elite athletes are characterized by a reduced cortical activation during the preparation of precise visuo-motor performance; (ii) in elite athletes, an optimal visuo-motor performance is related to a low cortical activation. To this aim, electroencephalographic (EEG; 56 channels; Be Plus EB-Neuro) data were recorded in 18 right-handed elite air pistol shooters and 10 right-handed non-athletes. All subjects performed 120 shots. The EEG data were spatially enhanced by surface Laplacian estimation. With reference to a baseline period, power decrease/increase of alpha rhythms during the preshot period indexed the cortical activation/deactivation (event-related desynchronization/synchronization, ERD/ERS). Regarding the hypothesis (i), low- (about 8-10 Hz) and high-frequency (about 10-12 Hz) alpha ERD was lower in amplitude in the elite athletes than in the non-athletes over the whole scalp. Regarding the hypothesis (ii), the elite athletes showed high-frequency alpha ERS (about 10-12 Hz) larger in amplitude for high score shots (50%) than for low score shots; this was true in right parietal and left central areas. A control analysis confirmed these results with another indicator of cortical activation (beta ERD, about 20 Hz). The control analysis also showed that the amplitude reduction of alpha ERD for the high compared with low score shots was not observed in the non-athletes. The present findings globally suggest that in elite athletes (experts), visuo-motor performance is related to a global decrease of cortical activity, as a possible index of spatially selective cortical processes ("neural efficiency").
Figures







References
-
- Babiloni F,Babiloni C,Carducci F,Fattorini L,Onorati P,Urbano A ( 1996): Spline Laplacian estimate of EEG potentials over a realistic magnetic resonance‐constructed scalp surface model. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 98: 363–373. - PubMed
-
- Babiloni F,Carducci F,Babiloni C,Urbano A ( 1998): Improved realistic Laplacian estimate of highly‐sampled EEG potentials by regularization techniques. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 106: 336–343. - PubMed
-
- Babiloni C,Babiloni F,Carducci F,Cincotti F,Cocozza G,Del Percio C,Moretti DV,Rossini PM ( 2002): Human cortical EEG rhythms during the observation of simple aimless movements. A high resolution EEG study. NeuroImage 17: 559–572. - PubMed
-
- Babiloni C,Miniussi C,Babiloni F,Carducci F,Cincotti F,Del Percio C,Sirello G,Sosta K,Nobre AC,Paolo M,Rossini PM ( 2004): Sub‐second “temporal attention” modulates alpha rhythms. A high‐resolution EEG study. Cognit Brain Res 19: 259–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

